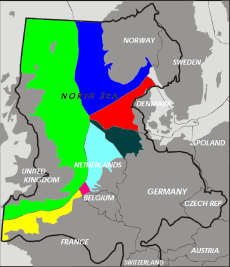
North Sea
| North Sea | |
|---|---|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: |
| Primary sources | Forth, Ythan, Elbe, Weser, Ems, Rhine/Waal, Meuse, Scheldt, Spey, Tay, Thames, Humber, Tees, Wear, Tyne |
| Basin countries | Norway, Denmark, Germany, Netherlands, Belgium, France and the U.K. (England, Scotland) |
| Max length | 960 kilometers (600 mi)[1] |
| Max width | 580 kilometers (360 mi)[1] |
| Surface area | 750,000 square kilometers (290,000 sq mi)[1] |
| Average depth | 95 meters (310 ft)[1] |
| Max depth | 700 meters (2,300 ft)[1] |
| Water volume | 94[1] |
| Salinity | 34 to 35 g salt per litre of water (0.34 to 0.35 pound/gallon (UK).[1] |
| Max temperature | 17 °C (60 °F)[1] |
| Min temperature | 6 °C (40 °F)[1] |
The North Sea is a marginal, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf. It is bordered by Great Britain to the west and southwest, northwest by the Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands, east and northeast by Norway and Denmark, Germany and the Netherlands to the southeast, with Belgium and France to the south. The Dover Strait and the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north connect it to the Atlantic Ocean. It is more than 970 kilometers (600 mi) long and 560 kilometers (350 mi) wide, with an area nearing 750,000 square kilometers (290,000 sq mi). A large part of the European drainage basin empties into the North Sea including water from the Baltic Sea.
Much of the sea's coastal features are the result of glacial movements. Deep fjords and sheer cliffs mark the Norwegian and the Scottish coastline. The southern coasts consist of sandy beaches and mudflats. Elaborate systems of dikes particularly in the Netherlands have been constructed to protect coastal areas from flooding.
The development of European civilization has been greatly affected by maritime traffic on the North Sea. The Roman Empire and the Vikings both extended their contemporaneous territories across the sea. The Hanseatic League, the Netherlands, and lastly the British Empire sought to dominate commerce both on the North Sea and through it. Then as now, the North Sea offers access to the markets and resources of the world. The sea has at times protected the British Isles from continental invasion and served as a springboard for growth of the nations bordering it. Historically it allowed for the interchange of people, goods, and ideas that fed the cultural development of northwestern Europe.
In recent decades, the Sea's importance has largely shifted from military and geopolitical concerns to economics and environmental. Traditional activities, such as fishing and shipping, have continued to grow and natural resources such as fossil fuels and wind energy, have been discovered and developed there.
History

Name
One of the initial namings was Septentrionalis Oceanus, or Northern Ocean which was cited by Pliny.[2] Other common names in use for long periods were the Latin terms Mare Frisicum[3], Oceanum- or Mare Germanicum[4] as well as their English equivalents, "Frisian Sea," "German Ocean," "German Sea" and "Germanic Sea" (from the Latin Mare Germanicum). Other names were Amalchium Mare, Britannie ef Frisie mare, Fresonicus Ocecnus, Magnum Mare, Occidentale Mare, Occidentalis Oceanus. By the late nineteenth century, these names were rare, scholarly usages.
Early history
The first records of marine traffic on the North Sea come from the Roman Empire, which began exploring the sea in 12 B.C.E. Great Britain was formally invaded in 43 C.E. and its southern areas incorporated into the Empire, beginning sustained trade across the North Sea and the English Channel. The Romans abandoned Britain in 410 and in the power vacuum they left, the Germanic Angles, Saxons, and Jutes began the next great migration across the North Sea during the Migration Period invading England.

The Viking Age began in 793 with the attack on Lindisfarne and for the next quarter-millennium the Vikings ruled the North Sea. In their superior longships, they raided, traded, and established colonies and outposts on the Sea's coasts. From the Middle Ages through the 15th century, the north European coastal ports exported domestic goods, dyes, linen, salt, metal goods and wine. The Scandinavian and Baltic areas shipped grain, fish, naval necessities, and timber. From the Mediterranean in this era would be high grade cloths, spices, and fruits. Commerce during this era was mainly undertaken by maritime trade due to underdeveloped roadways.
In the 13th century the Hanseatic League, though centered on the Baltic Sea, started to control most of the trade through important members and outposts on the North Sea. The League lost its dominance in the 16th century, as neighboring states took control of former Hanseatic cities and outposts and internal conflict prevented effective cooperation and defense. Furthermore, as the League lost control of its maritime cities, new trade routes emerged which provided Europe with Asian, The American, and African goods.
Early modern period
The seventeenth century Dutch Golden Age during which Dutch herring, cod and whale fisheries reached an all time high saw Dutch power at its zenith. Important overseas colonies, a vast merchant marine and a powerful navy made the Dutch the main challengers to an ambitious England, which also saw its future in these three spheres. This rivalry was the root cause of the first three Anglo-Dutch Wars between 1652 and 1673.[5] Despite Dutch victories in these and other wars, the ascension of the Dutch prince William to the English throne caused a dramatic shift in commercial, military, and political power from Amsterdam to London. By the end of the War of Spanish Succession in 1714, the Dutch were no longer major players in European politics.
Several conflicts involved disruption of North Sea maritime trade, none of which had a decisive effect on the war's outcome: the French and British cut off Russia's Baltic ports during the Crimean War and Prussia's coasts were blockaded in the Firstand Second Schleswig Wars as well as the Franco-Prussian War. The British did not face a challenge to their dominance of the North Sea until World War I broke out in 1914.
Modern era

Tensions in the North Sea were again heightened in 1904 by the Dogger Bank incident, in which Russian naval vessels mistook British fishing boats for Japanese ships and fired on them, and then upon each other.[6] During the First World War, Great Britain's Grand Fleet and Germany's Kaiserliche Marine faced each other on the North Sea, which became the main theater of the war for surface action. Britain's larger fleet was able to establish an effective blockade for most of the war that restricted the Central Powers' access to many crucial resources. Major battles included the Battle of Heligoland Bight, the Battle of the Dogger Bank, the Battle of Jutland, and the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight. Britain, though not always tactically successful, maintained the blockade and thus kept the High Seas Fleet in port. Conversely, the German navy remained a threat that kept the vast majority of Britain's capital ships in the North Sea. World War I was also the first in which submarine warfare was used extensively and a number of submarine actions occurred in the North Sea.
The Second World War also saw action in the North Sea, though it was restricted more to submarines and smaller vessels such as minesweepers, and torpedo boats and similar vessels. In the last years of the war and the first years thereafter, hundreds of thousands of tons of weapons were disposed of by being sunk in the North Sea.[7]
After the war, the North Sea lost much of its military significance because it is bordered only by NATO member-states. However, it gained significant economic importance in the 1960s as the states on the North Sea began full-scale exploitation of its oil and gas resources. The North Sea continues to be an active trade route.
Archaeological sites
Several major archaeological finds were made in recent years in areas under the North Sea. From 2002 through 2005, Danish and Swedish scientists studied in secret the ruins of an ancient city several dozen square kilometers in size.[8]
In 2007, archaeologists uncovered a huge, prehistoric "lost country," from the east coast of Britain, to the Shetland Islands, and to Scandinavia.[9]
The third major find occurred in February of the following year when an amateur archaeologist dredged up Palaeolithic hand axes in the area between present-day Britain and Holland, leading scientists to believe that humans lived alongside mammoths approximately 100,000 years ago off Great Yarmouth.[10]
Geography
Eng Ch=English Channel
The North Sea is bounded by the east coasts of England and Scotland to the west, and the northern and central European mainland to the east and south, including Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively. In the north, it opens in a widening funnel shape to the Norwegian Sea, which lies in the very northeastern part of the Atlantic.
The surface area of the North Sea is approximately 750,000 square kilometers (290,000 sq mi)[1] with a volume of around 94,000 cubic kilometers (23,000 cu mi).[1] Around the edges of the North Sea are sizable islands and archipelagos, including Shetland, Orkney, and the Frisian Islands.
Submarine topography
For the most part, the sea lies on the European continental shelf. The only exception is the Norwegian trench, which reaches from the Stad peninsula in Sogn og Fjordane to the Oslofjord. At its deepest point in the Skagerrak, off Arendal, it reaches a depth of 700 meters (2,300 ft).[11] The trench is not a subduction-related oceanic trench, where one tectonic plate is being forced under another. It is mainly a deep erosional scour, while the western part follows the North-South line of an old Rift Valley formed during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
To the east of Great Britain lies the Dogger Bank, a vast moraine, or accumulation of unconsolidated glacial debris, which in some places is only 15 to 30 m (50 - 100 ft) below the surface of the sea.[12]
The Silver Pit is a valley-like depression 45 km (27 mi) east of Spurn Head in England that has been recognized for hundreds of years by fishermen. Nearby is the Silverpit crater, a controversial structure initially proposed to be an impact crater, though another interpretation is that it may result from the dissolution of a thick bed of salt which permitted the upper strata to collapse. Devil's Hole is a group of trenches, around 120 meters (390 ft) deeper than the surrounding sea floor, about 200 km (125 mi) east of Dundee, Scotland.[13]
"The Long Forties" denotes an area of the northern North Sea that is fairly consistently forty fathoms (73 m) deep and thus, on a nautical chart with depth shown in fathoms, a long area with 33, 34, 35, "40" notations.[14] It is located between the northeast coast of Scotland and the southwest coast of Norway. The Broad Fourteens are an area of the southern North Sea that is between 11 (20 m) and 14 fathoms (26 m) deep and thus a broad area with many "14" notations. It is located off the coast of the Netherlands and south of the Dogger Bank.
Geology
Shallow epicontinental seas like the current North Sea have long existed on the European continental shelf. The rifting that formed the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, from about , caused tectonic uplift in the British Isles. Since then, a shallow sea has almost continuously existed between the highs of the Fennoscandian Shield and the British Isles. This precursor of the current North Sea has grown and shrunk with the rise and fall of the eustatic sea level during geologic time. At times it was connected with other shallow seas, such as the sea above the Paris Basin to the southwest, the Paratethys Sea to the southeast, or the Tethys Ocean to the south.[15]
During the Late Cretaceous, about , all of modern mainland Europe except for Scandinavia was a scattering of islands. By the Early Oligocene, , the emergence of Western and Central Europe had almost completely separated the North Sea from the Tethys Ocean, which gradually shrank to become the Mediterranean Sea as Southern Europe and Southwest Asia became dry land.[16]
The North Sea was cut off from the English Channel by a narrow land bridge until that was breached by at least two catastrophic floods between 450,000 and 180,000 years ago. Since the start of the Quarternary period about , the eustatic sea level has fallen during each glacial period and then risen again. Every time the ice sheet reached its greatest extent, the North Sea became almost completely dry. The present-day North Sea coastline formed when, after the Last Glacial Maximum (the peak of the glaciation during the last ice age) 20,000 years ago, the sea began to flood the European continental shelf. The North Sea coastline still undergoes changes following changes in the worldwide sea level, tectonic movements, storm surges, erosion, the rise and fall of sea levels, shingle drifts as well as the deposition of sands and clastics in paralic environments.
Tectonic structure
The Mesozoic structures underneath the North Sea can be seen as a failed rift. After initial crustal extension and the formation of rift basins during the Triassic and Jurassic periods, the extension concentrated on the other side of the British Isles, which would create the northern Atlantic Ocean. The Cretaceous period even saw some inversion of the rift basins. From the Oligocene onward, tensions in the European crust caused by the Alpine orogeny to the south cause a new, more modest phase of extension. Some grabens in the area are still active.
The subsurface of the North Sea area is dominated by grabens: the northwest-southeast oriented Lower Rhine Graben under the southern North Sea and the Netherlands, the north-south oriented North Sea Central Graben that begins north of the Dutch coast and ends in the region east of Scotland, and the Viking Graben along the southeast Norwegian coast. The Horn Graben is a smaller graben east of the Central Graben and in front of the Danish coast. A larger graben is found in the subsurface below the Skagerrak, this north-south structure is called the Bamble-Oslo Graben. The Viking Graben is separated from the Faeroe Through below the Atlantic by the Shetland Platform, the two structures join in the area northeast of the Shetland Islands.
Natural history
Fish and shellfish
Copepods and other zooplankton are plentiful in the North Sea. These tiny organisms are crucial elements of the food chain supporting many species of fish. The North Sea is home to about 230 species of fish. Cod, haddock, whiting, saithe, plaice, sole, mackerel, herring, pouting, sprat, and sandeel are all very common and the target of commercial fishing. Due to the various depths of the North Sea trenches and differences in salinity, temperature, and water movement, some fish reside only in small areas of the North Sea. The blue-mouth redfish and rabbitfish are examples of these.
Crustaceans are also commonly found throughout the sea. Norway lobster, deep-water prawns, and brown shrimp are all commercially fished, but other species of lobster, shrimp, oyster, mussels and clams are all found. Recently non-indigenous species have become established including the Pacific oyster and Atlantic jackknife clam.
Birds
The coasts of the North Sea are home to nature reserves including the Ythan Estuary, Fowlsheugh Nature Preserve, and Farne Islands in the UK and The Wadden Sea National Parks in Germany. These locations provide breeding habitat for dozens of bird species. Tens of millions of birds make use of the North Sea for breeding, feeding, or migratory stopovers every year. Populations of Northern fulmars, Black-legged Kittiwakes, Atlantic puffins, razorbills, and species of petrels, gannets, seaducks, loons (divers), cormorants, gulls, auks, and terns, and many other seabirds make these coasts popular for birdwatching.
Marine mammals

The North Sea is also home to marine mammals. Common seals, grey seals can be found along the coasts, at marine installations, and on islands. The very northern North Sea islands like the Shetlands are occasionally home to a larger variety of pinnipeds including bearded, harp, hooded and ringed seals, and even walrus. North Sea cetaceans include Harbour porpoises, common dolphins, bottlenose dolphins, Risso's dolphins, long-finned pilot whales and white-beaked dolphins, minke whales, killer whales, and sperm whales.
Flora
Plant species in the North Sea include species of wrack, among them bladder wrack, knotted wrack, and serrated wrack. Algae, including kelp, such as oarweed and laminaria hyperboria, and species of maerl are found as well. Nori, (P. umbilicalis) is found along the coast of the North Sea and is a widely marketed edible seaweed. Eelgrass, formerly common in the entirety of the Wadden Sea, was nearly wiped out in the twentieth century by a disease and has struggle to reestablish itself. Similarly, sea moss used to coat huge tracts of ocean floor, but have been damaged by trawling and dredging have diminished its habitat and prevented its return. Invasive Japanese seaweed has spread along the shores of the sea clogging harbors and inlets and has become a nuisance.
Hydrology
Basic data

The average temperature in summer is 17 °C (63 °F) and 6 °C (43 °F) in the winter. Global warming has been attributed to a rise in the average temperature of the North Sea.[18]
Temperature varies according to water depth. Channel water is 1 °C (34 °F) to 2 °C (36 °F) colder than water on the coastal shores during summer months. However, channel water is 1 °C (34 °F) to 2 °C (36 °F) warmer than water on the coast shores in the winter months. In summer, the temperatures rise to maxima of around 15 °C (59 °F) to 17 °C (63 °F), and in the winter the temperature maximum is between 5 °C (41 °F) to 7 °C (45 °F). The salinity averages between 34 to 35 g salt per litre of water. The salinity has the highest variability where there is fresh water inflow, such as at the Rhine and Elbe estuaries, the Baltic Sea exit and along the coast of Norway.
Around 184 million people live in the catchment area of the rivers that flow into the North Sea. This area contains one of the world's greatest concentrations of industry.[19]
Water circulation
The main pattern to the flow of water in the North Sea is a counter-clockwise rotation along the edges. The North Sea is a part of the Atlantic Ocean, receiving the majority of its content from the northwest opening, and a lesser portion from the smaller opening at the English Channel. These tidal currents leave along the Norwegian coast. Surface and deep water currents may move in different directions. Low salinity surface coastal waters move offshore, and deeper, denser high salinity waters move in shore.
Water from the Gulf Stream flows in both through the English Channel towards Norway, and around the north of Britain, moving south along the British coast. From the south-moving current smaller currents are pulled off eastwards into the central North Sea. Another significant current sweeps south in the eastern part of the Sea. This is cold North Atlantic water and is strongest in late spring and early summer when the British offshore waters remain cool while the sea off the Netherlands and Germany starts warming up. Water from the Channel, and water flowing out of the Baltic Sea eventually move north along the Norwegian coast back into the Atlantic in what is called the Norwegian Current.
Tides
There are three factors which influence tidal waves in sea basins which possess weak wave systems; the sea oscillation period, the ocean tide range approaching the North Sea and the entrance dimensions between the ocean and the North Sea.[20]
The Kelvin tide of the Atlantic Ocean is a semidiurnal wave which travels northward. Some of the energy from this wave travels through the English Channel into the North Sea. The wave still travels northward in the Atlantic Ocean, and once past the British Isles, the Kelvin wave turns east and south and once again enters into the North Sea. The North Sea located on the continental shelf has different waves than those in deep ocean water. The wave speeds are diminished and the wave amplitudes are increased. In the North Sea there are two amphidromic systems and a third incomplete amphidromic system. At an amphidromic point the rise and fall of tidal waves is zero due to canceling of tidal waves, and the semidiurnal high and low tides rotate around these points twice in a tidal day. As a result, the tidal range in southern Norway is less than half a meter (1.5 ft), but increases the further any given coast lies from the amphidromic point.[21] Shallow coasts and the funnel effect of narrow straits increase the tidal range. The tidal range is at its greatest at The Wash on the English coast, where it reaches 6.5 metres (21 ft). In the North Sea the average tide difference in wave amplitude is between 0 to 8 meters (0 to 26 ft).[1]
Coasts
The eastern and western coasts of the North Sea are jagged, as they were stripped by glaciers during the ice ages. The coastlines along the southernmost part are soft, covered with the remains of deposited glacial sediment, which was left directly by the ice or has been redeposited by the sea. The Norwegian mountains plunge into the sea, giving birth, north of Stavanger, to deep fjords and archipelagos. South of Stavanger, the coast softens, the islands become fewer. The eastern Scottish coast is similar, though less severe than Norway. Starting from Flamborough Head in the north east of England, the cliffs become lower and are composed of less resistant moraine, which erodes more easily, so that the coasts have more rounded contours. In Holland, Belgium and in the east of England (East Anglia) the littoral is low and marshy. The east coast and southeast of the North Sea (Wadden Sea) have coastlines that are mainly sandy and straight owing to longshore currents, particularly along Belgium and Denmark.
Northern fjords, skerries, and cliffs
The northern North Sea coasts bear the impression of the enormous glaciers which covered them during the Ice Ages and created a split, craggy coastal landscape. Fjords arose by the action of glaciers, which dragged their way through them from the highlands, cutting and scraping deep trenches in the land. During the subsequent rise in sea level, they filled with water. They very often display steep coastlines and are extremely deep for the North Sea. Fjords are particularly common on the coast of Norway.
Firths are similar to fjords, but are generally shallower with broader bays in which small islands may be found. The glaciers that formed them influenced the land over a wider area and scraped away larger areas. Firths are to be found mostly on the Scottish and northern English coasts. Individual islands in the firths, or islands and the coast, are often joined up by sandbars or spits made up of sand deposits known as “tombolos.”
Towards the south the firths give way to a cliff coast, which was formed by the moraines of Ice Age glaciers. The horizontal impact of waves on the North Sea coast gives rise to eroded coasts. The eroded material is an important source of sediment for the mudflats on the other side of the North Sea. The cliff landscape is interrupted in southern England by large estuaries with their corresponding mud and marshy flats, notably the Humber and the Thames.
There are skerries in southern Norway and on the Swedish Skagerrak coast. Formed by similar action to that which created the fjords and firths, the glaciers in these places affected the land to an even greater extent, so that large areas were scraped away. The coastal brim (Strandflaten), which is found especially in southern Norway, is a gently sloping lowland area between the sea and the mountains. It consists of plates of bedrock, and often extends for kilometers, reaching under the sea, at a depth of only a few meters.
Southern shoals and mudflats
The shallow-water coasts of the southern and eastern coast up to Denmark were formed by ice age activity, but their particular shape is determined for the most part by the sea and sediment deposits.
The Wadden Sea stretches between Esbjerg, Denmark in the north and Den Helder, Netherlands in the west. This landscape is heavily influenced by the tides and important sections of it have been declared a National Park. The whole of the coastal zone is shallow; the tides flood large areas and uncover them again, constantly depositing sediments. The Southern Bight has been especially changed by land reclamation, as the Dutch have been especially active.
Tidal forces have formed the Frisian Islands. In the micro tidal area, (a tidal range of up to 1.35 meters (4.4 ft), such as on the Dutch or Danish coasts,[22] barrier beaches with dunes are formed. In the mesotidal area (a tidal range of between 1.35 and 2.90 m (4.43-9.5 ft), barrier islands are formed in the macrotidal area (above 2.9 meters (9.5 ft) tidal range), such as at the mouth of the Elbe, underwater sandbanks form. A soft rock coast is formed in the meso-macro tidal areas located in the southern North Sea. These soft rock coastal bedrock plains are interspersed with soft rock (shale and sandstone) cliffs.
The small, historically strategic island of Heligoland was not formed by sediment deposition; it is considerably older and is composed of early Triassic sandstone.[23]
Storm tides
Storm tides threaten, in particular, the coasts of the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, and Denmark. These coasts are quite flat, so even a relatively small increase in the water levels is sufficient to put large stretches of land under water.
Storm surges are caused by changes in barometric pressure combined with strong wind-created wave action. The first recorded storm tide flood was the Julianenflut, on February 17, 1164.[24] In its wake the Jadebusen began to form.
A storm tide in 1228 is recorded to have killed more than 100,000 people.[25] In 1362, the Second Marcellus Flood, also known as the Grote Mandrenke, hit the entire southern coast of the North Sea. Chronicles of the time again record more than 100,000 deaths as large parts of the coast were lost permanently to the sea, including the now legendary lost city of Rungholt.[26]
The coastline of the North Sea changed again following the flood of 1825; the Jutland Peninsula is now called the North Jutlandic Island. In the twentieth century, the North Sea flood of 1953 flooded several nations' coasts and cost more than 2,000 lives. The North Sea flood of 1962 caused the deaths of 315 citizens of Hamburg. The "Century Flood" of 1976 and the "North Frisian Flood" of 1981 brought the highest water levels measured to date on the North Sea coast, but because of the dikes built and improved after the flood of 1962, these led only to property damage.
Tsunamis
The Storegga Slides were a series of underwater landslides, in which a piece of the Norwegian continental shelf slid into the Norwegian Sea. The immense landslips occurred between 8150 and 6000 B.C.E., and caused a tsunami up to 20 meters (66 ft) high that swept through the North Sea, having the greatest effect on Scotland and the Faeroe Islands.[27]
The Dover Straits earthquake of 1580 is among the first recorded earthquakes in the North Sea and caused extensive damage in as far north as London England both through its tremors and a tsunami.[28] The largest earthquake ever recorded in the United Kingdom was the 1931 Dogger Bank earthquake, which measured 6.1 on the Richter Scale and caused a tsunami that flooded parts of the British coast.[29]
Coastal preservation
The southern coastal areas were originally amphibious. The land included countless islands and islets which had been divided by rivers, streams, and wetlands and areas of dry land were regularly flooded. In areas especially vulnerable to storm tides, people settled first on natural areas of high ground such as spits and Geestland. As early as 500 B.C.E., people were constructing artificial dwelling hills several meters high. It was only around the beginning of the High Middle Ages, in 1200 C.E., that inhabitants began to connect single ring dikes into a dike line along the entire coast, thereby turning amphibious regions between the land and the sea into permanent solid ground. The modern form of the dikes began to appear in the 17th and 18th centuries, built by private enterprises in the Netherlands. The Dutch dike builders exported their designs to other North Sea regions. The North Sea Floods of 1953 and 1962 were impetus for further raising of the dikes as well as the shortening of the dike line through land reclamation and river weirs so as to present as little surface area as possible to the punishment of the sea and the storms. Currently, 27 percent of the Netherlands is below sea level protected by dikes, dunes, and beach flats.[30]
Coastal preservation today consists of several levels. The dike slope reduces the energy of the incoming sea, so that the dike itself does not receive the full impact. Dikes that lie directly on the sea are especially reinforced. The dikes have, over the years, been repeatedly raised, sometimes up to 9 meters (30 ft) and have become flatter in order to better reduce the erosion of the waves. Behind the dike, there generally runs an access road and a thinly inhabited area. In many places, another dike follows after several kilometers. Where the dunes are sufficient to protect the land behind them from the sea, these dunes are planted with beach grass to protect them from erosion by wind, water, and foot traffic.
Economy
Political status
The countries bordering the North Sea all claim the 12 nautical miles (22 kilometres) of territorial waters within which they have exclusive fishing rights. The Common Fisheries Policy of the European Union (EU) exists to coordinate fishing rights and assist with disputes between EU states and the EU border state of Norway.
After the discovery of mineral resources in the North Sea, Norway claimed its rights under the Convention on the Continental Shelf. The other countries on the sea followed suit. These rights are largely divided along the median line. The median line is defined as the line "every point of which is equidistant from the nearest points of the baselines from which the breadth of the territorial sea of each State is measured."[31] The ocean floor border between Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark was only reapportioned after protracted negotiations and a judgment of the International Court of Justice.
Oil and gas
As early as 1859, oil was discovered in onshore areas around the North Sea and natural gas as early as 1910.
In 1958, geologists discovered a natural gas field in Slochteren in the Dutch province of Groningen and it was suspected that more fields lay under the North Sea. However, at this point, the rights to natural resource exploitation on the high seas were still under dispute. Test drilling began in 1966 and then, in 1969, Phillips Petroleum Company discovered the Ekofisk oil field (now Norwegian), which at that point, was one of the 20 largest in the world, and turned out to be distinguished by valuable, low-sulphur oil. Commercial exploitation began in 1971 with tankers and, after 1975, by a pipeline, first to Teesside, England and then, after 1977, also to Emden, Germany.
The exploitation of the North Sea oil reserves began just before the 1973 oil crisis, and the climb of international oil prices made the large investments needed for extraction much more attractive. In the 1980s and 1990s, further discoveries of large oil fields followed. Although the production costs are relatively high, the quality of the oil, the political stability of the region, and the nearness of important markets in western Europe has made the North Sea an important oil producing region.
The largest single humanitarian catastrophe in the North Sea oil industry was the destruction of the offshore oil platform Piper Alpha in 1988 in which 167 people lost their lives.[32]
The fires on the Piper Alpha burned off most of the hydrocarbons on board and released from the disrupted wells. However, a major blowout in 1977 in the Ekofisk field resulted in oil flowing unimpeded into the sea for a week before it was capped; estimates of the amount of oil released to the environment vary between 86,000 and 202,380 barrels (between 10,000 to 30,000 tonnes, depending on the density of the oil).[33]
Besides the Ekofisk oil field, the Statfjord oil field is also notable as it was the cause of the first pipeline to span the Norwegian trench. The largest natural gas field in the North Sea, Troll Field, lies in the Norwegian trench dropping over 300 meters (980 ft) requiring the construction of the enormous Troll A platform to access it.
The price of Brent Crude, one of the first types of oil extracted from the North Sea, is used today as a standard price for comparison for crude oil from the rest of the world.[34]
Fishing
Fishing in the North Sea is concentrated in the southern part of the coastal waters. The main method of fishing is trawling.
In 1995, 3.5 million tonnes of fish and shellfish were caught by Belgian fisheries, which was 1 percent of the North Sea volume of fish caught.[35] Besides the fish caught, it is estimated that 1,000,000 metric tons (1,150,000 S/T) of unmarketable by-catch are caught, 250,000 sea turtles and 7,000 harbor porpoises are also part of the bycatch.[36][37]
In recent decades, overfishing has left many fisheries unproductive, disturbing the marine food chain dynamics and costing jobs in the fishing industry. Herring, cod and plaice fisheries may soon face the same plight as mackerel fishing, which ceased in the 1970s due to overfishing.
Since the 1960s, various regulations have attempted to protect the stocks of fish such as limited fishing times and limited numbers of fishing boats, among other regulations. However, these rules were never systematically enforced and did not bring much relief. Since then, the United Kingdom and Denmark, two important fishing nations, became members of the EU, and have attempted, with the help of the Common Fisheries Policy, to bring the problem under control.
Mineral resources

In addition to oil, gas, and fish, the states along the North Sea also take millions of cubic meters per year of sand and gravel from the ocean floor. These are used for construction projects, sand for beaches, and coast protection. The largest extractor of sand and gravel in 2003 was far and away the Netherlands (around 30 million m³ {322 million sq ft}) with Denmark a distant second (around 10 million m³ {110 million sq ft} from the North Sea).
Rolled pieces of amber, usually small but occasionally of very large size, may be picked up on the east coast of England, having been washed up from deposits under the North Sea. On the other side of the North Sea, amber is found at various localities on the coast of the Netherlands and Denmark. Amber was also found on the Baltic coast across northern Europe. Some of the amber districts of the Baltic and North Sea were known in prehistoric times, and led to early trade with the south of Europe along the so-called Amber Road.
Renewable energy
Due to the strong prevailing winds, countries on the North Sea, particularly Germany and Denmark, have used the areas near the coast for wind-driven electricity production since the 1990s. Offshore wind turbines appeared first off the English coast near Blyth in 2000 and then off the Danish coast in 2002 near Horns Rev. Others have been commissioned, including Windpark Egmond aan Zee (OWEZ) and Scroby Sands and more are in the planning phase. Offshore wind farms have met some resistance. Concerns have arisen about shipping collisions and damage to the ocean ecology, particularly by the construction of the foundations. Nonetheless, the first deep water turbines in Scotland are under commission for Talisman Energy, who are installing two large machines 25 kilometers (16 mi) offshore adjacent to the Beatrice oilfield. These turbines are 88 meters (290 ft) high with the blades 63 meters (210 ft) long and will have a capacity of 5 megawatts (MW) each, making them the largest in the world.[38][39]
Energy production from the sea itself is still in a pre-commercial stage. The southern parts of the North Sea do not have sufficient tidal range to harness energy usefully. The Norwegian coast and the intersection with the Irish Sea could be found suitable for waves or ocean currents to provide power. The European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC) based at Stromness in Orkney is a Scottish Government-backed research facility. They have installed a wave testing system at Billia Croo on the Orkney mainland and a tidal power testing station on the nearby island of Eday. Since 2003, a Wave Dragon overtopping system prototype for harnessing wave power is deployed in the Nissum Bredning fjord of northern Denmark.
Tourism
The beaches and coastal waters of the North Sea are popular destinations for tourists. The Belgian, Dutch, German, and Danish coasts are especially developed for tourism. While many of the busiest British beach resorts are on the south coast, the British east coast also has important beach resorts.
The climatic conditions on the North Sea coast are often claimed to be especially healthful. As early as the nineteenth century, travellers used their stays on the North Sea coast as curative and restorative vacations. The sea air, temperature, wind, water, and sunshine are counted among the beneficial conditions that are said to activate the body's defenses, improve circulation, strengthen the immune system, and have healing effects on the skin and the respiratory system.
Marine traffic
The North Sea is important for marine traffic and experiences some of the densest concentrations of ships in the world. Great ports are located along its coasts: Rotterdam, the third busiest port in the world by tonnage, Antwerp and Hamburg, both in the top 25, Bremen/Bremerhaven and Felixstowe, both in the top 30 busiest container seaports,[40] as well as the Port of Bruges-Zeebrugge, Europe's leading RoRo port.[41]
All major ports have easy access to the various sea lanes of the North Sea, which are monitored, well-regulated, and regularly dredged. Traffic in the North Sea can be difficult. Fishing boats, oil and gas platforms as well as merchant traffic from Baltic ports share routes on the North Sea. The possibility of bottlenecks at the Dover Strait, which sees more than 400 vessels a day and the Kiel Canal, which averages more than 100 per day plus sport traffic can add to the difficulty.
The North Sea coasts are home to numerous canals and canal systems to facilitate traffic between and among rivers, artificial harbors, and the sea. The Kiel Canal, connecting the North Sea with the Baltic Sea, is the most heavily used artificial seaway in the world. It opened on June 20, 1895 and saves an average of 250 nautical miles (463 kilometres), instead of the voyage around the Jutland Peninsula. [42] The North Sea Canal connects Amsterdam with the North Sea.
Concerns


The North Sea is one of the world's busiest maritime areas. It is surrounded by the densely populated, highly industrialized countries of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway and the United Kingdom. Maritime traffic is of significant importance because it is one of the most frequently traveled seas with two of the world's largest ports, Rotterdam and Hamburg, located on its coasts.
Its coastal zone is used extensively for agriculture and recreation, while activities in the Sea include fishing and the extraction of sand and gravel. Offshore activities related to the Sea include exploitation of oil and natural gas reserves, including the laying of pipelines.[43]
A biologically rich area, industrialization along the Sea's coasts poses a threat to its wildlife. Species including flamingos, pelicans, and Great Auk were once found along the southern shores of the North Sea, and became extinct in the latter years of the second millennium.[44] Gray whale also resided in the North Sea but were driven to extinction in the Atlantic in the 1600s.[45] Other species have seen dramatic declines in population; right whales, sturgeon, shad, rays, skates and salmon among other species once common to the North Sea well into the nineteenth and twentieth century. Most stocks of commercially exploited fish in the North Sea are in a precarious condition. In an effort to save many species from extinction, United Nations Environmental Programme recommended that the Sea's fishing fleets be reduced by 40 percent to match fish resources.[46]
A variety of factors have contributed to decreasing populations of North Sea fauna. The introduction of non-indigenous species, industrial and agricultural pollution, overfishing and trawling, dredging, human-induced eutrophication, construction on coastal breeding and feeding grounds, sand and gravel extraction, offshore construction, and heavy shipping traffic all threaten marine life in the North Sea.
In recent decades, action has been taken by the border countries to address many of these threats. The OSPAR convention was created in 1992 as an expansion of the 1972 Oslo Convention. It is managed by the OSPAR commission and has taken action to counteract the harmful effects of human activity on wildlife in the North Sea and preserve many endangered species.[47] All North Sea border states are signatories of the MARPOL 73/78 Accords. Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands also have a trilateral agreement for the protection of the Wadden Sea, or mudflats, which run along the coasts of the three countries on the southern edge of the North Sea.[48] The North Sea Region Programme was established in 2007 in order to expand the scope of territorial cooperation, connecting nations, and incorporating policy level planning and the long lasting and tangible effects of projects. While the program deals largely with economics, it also considers environmental impacts on the Sea.[49]
Continued development of the North Sea Region will require cooperation among its border nations, and must take into consideration not only economic growth, but the health of the North Sea's environment.
Notes
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Safety at Sea. 2008. About the North Sea: Key facts Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Duane W. Roller. 2006. Through the pillars of Herakles: Greco-Roman exploration of the Atlantic. (New York: Routledge. ISBN 9780415372879)
- ↑ Stephan Thernstrom. 1980. Harvard Encyclopedia of American ethnic groups. (Cambridge, MaA: Belknap Press of Harvard University. ISBN 9780674375123)
- ↑ William H. Sherman, 1995. John Dee the politics of reading and writing in the English Renaissance. Massachusetts studies in early modern culture. (Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 9781558490703)
- ↑ Ronald Findlay and Kevin H. O'Rourke. 2007. Power and plenty: trade, war, and the world economy in the second millennium.( The Princeton economic history of the western world.) (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691118543)
- ↑ R. M. Connaughton. 1991. The War of the Rising Sun and tumbling bear: a military history of the Russo-Japanese War 1904-5. (London: Routledge. ISBN 9780415071437)
- ↑ Marc Koch and Wolfgang Ruck. 2006. "Securing and Remediation Concepts for Dumped Chemical and Conventional Munitions in the Baltic Sea." Defence Science and Technology Laboratory.
- ↑ Michael Martinez. March 31, 2005. Danish, Swedish archaeologists announce vast underground city in North Sea Xenite.Org. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Sean Coughlan. April 23, 2007. Archaeologists are uncovering a huge prehistoric "lost country" hidden below the North Sea. BBC News. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Brian Handwerk. March 17, 2008. Stone Age Hand Axes Found at Bottom of North Sea National Geographic News. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Vittorio Barale and Martin Gade. 2008. "The European and Marginal Seas: An Overview." chapter in Remote sensing of the European seas. (Dordrecht: Springer. ISBN 9781402067716)
- ↑ Maptech Online MapServer. Dogger Bank Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Alan Fyfe, The Devil's Hole in the North Sea The Edinburgh Geologist 14 (Autumn 1983).
- ↑ Society for the Benefit of the Sons and Daughters of the Clergy. 1845. The New statistical account of Scotland. (Edinburgh: W. Blackwood and Sons.) Online version books.google. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Trond H. Torsvik, Daniel Carlos, Jon Mosar, L. Robin M. Cocks and Tarjei N. Malme. November 2004. Global reconstructions and North Atlantic paleogeography 440 Ma to Recent Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ A. Gilbert Smith, David G. Smith, and B. M. Funnell. 2004. Atlas of Mesozoic and Cenozoic coastlines. (New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521602874)
- ↑ NASA Earth Observatory. September 22, 2008. The Strait of Dover Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Agence France-Presse. November 14, 2006.Global Warming Triggers North Sea Temperature Rise Retrieved December 1, 2008.
- ↑ International Center for the Environmental Management of Enclosed Coastal Seas. North Sea Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ D. T. Pugh, 2004. Changing sea levels: effects of tides, weather, and climate. (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521532181)
- ↑ Paul Tett, February 19, 2003, Marine Biology 2. Water layering and water movements Napier University School of Life Sciences. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Florenz A. P. Hollebrandse. Temporal development of the tidal range in the southern North Sea Delft University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Joachim Jaeck. July 21, 2008. History Exotics on Heligoland. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Economy-point.org. 2006. Julianenflut Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ RenéMorin. October 2, 2008. Social, economical and political impact of Weather Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Das Wissensmagazin. June 12, 2008. Der Untergang: Die Grote Manndränke - Rungholt Nordsee Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Axel Bojanowski. October 11, 2006. Tidal Waves in Europe? Study Sees North Sea Tsunami Risk Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ L. Ottemoller, B. Baptie, and N. J. P. Smith. 2008. "Tectonic implications of the 28 April 2007 MW4.0 Dover Straits earthquake." Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 10, EGU2008-A-11738, 2008 SRef-ID: 1607-7962/gra/EGU2008-A-11738.
- ↑ Cecile Baeteman. May 7, 2007. A tsunami in Belgium? Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Matt Rosenberg. January 30, 2007. Polders and Dykes of the Netherlands: The Reclamation of Land in the Netherlands About.com - The New York Times Company. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ The Multilaterals Project, The Fletcher School, Tufts University. April 29, 1958. Convention on the Continental Shelf, Geneva Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ BBC News. On This Day 6 July 1988: Piper Alpha oil rig ablaze BBC News. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Oil Rig Disasters.Ekofisk Bravo Platform Blowout versatel.nl. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Investopedia ULC. North Sea Brent Crude Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences. Fishing Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Ningbo CNC Fish Gear Manufacturing Co. November 5, 2008. One Million Tons of North Sea Fish Discarded Every Year Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Environmental News Service, March 20, 2002, Fish dumping 'will ruin industry' Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Talisman Energy. February 14, 2006. Beatrice Wind Farm Demonstrator Project Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Renewable Energy. Worlds Largest Wind Turbine Generator Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ American Association of Port Authorities. World Port Rankings 2006 Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Scientia Technologies Corporation. Port Authority Bruges-Zeebrugge Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ Kiel Canal. Kiel Canal Traffic Data Retrieved January 12, 2009.
- ↑ OSPAR Commission. Region II - Greater North Sea Retrieved January 25, 2009.
- ↑ Ransom A. Myers, October 27, 2006, Extinct / extirpated species Future of Marine Animal Populations/Census of Marine Life. Retrieved November 24, 2008.
- ↑ The Extinction Website. January 19, 2008. Species Info - Atlantic Grey Whale.
- ↑ United Nations Environmental Programme. The State of the Environment - Europe and Central Asia Retrieved January 25, 2009.
- ↑ European Union. May 9, 2006. OSPAR Convention Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Stevens & Associates. June 1, 2006. Wadden Sea Region Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved January 4, 2009.
- ↑ North Sea Region Programme. Programme Strategy and Priorities Retrieved January 25, 2009.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Barale, Vittorio, and Martin Gade. 2008. "The European and Marginal Seas: An Overview." chapter in Remote sensing of the European seas. Dordrecht: Springer. ISBN 9781402067716.
- Connaughton, R. M. 1991. The war of the rising sun and tumbling bear: a military history of the Russo-Japanese War 1904-5. London: Routledge. ISBN 9780415071437
- De Batist, M., and P. Jacobs. 1996. Geology of siliciclastic shelf seas. (Geological Society special publication, no. 117.) London: Geological Society. ISBN 9781897799710
- Findlay, Ronald, and Kevin H. O'Rourke. 2007. Power and plenty: trade, war, and the world economy in the second millennium. (The Princeton economic history of the Western World.) Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691118543
- Hardisty, J. 1990. The British seas: an introduction to the oceanography and resources of the north-west European continental shelf. London [England]: Routledge. 9780415035866
- Ilyina, Tatjana P. 2007. The fate of persistent organic pollutants in the North Sea Multiple year model simulations of [gamma]-HCH, [alpha]-HCH and PCB 153. (Hamburg studies on maritime affairs, v. 7.) Berlin: Springer. ISBN 9783540681632
- Karlsdóttir, Hrefna M. 2005. Fishing on common grounds: the consequences of unregulated fisheries of North Sea herring in the postwar period. Göteborg: Ekonomisk-Historiska Institutionen vid Göteborgs Universitet. ISBN 9185196622
- Roller, Duane W. 2006. Through the pillars of Herakles: Greco-Roman exploration of the Atlantic. New York: Routledge. ISBN 9780415372879
- Sherman, William H. 1995. John Dee; the politics of reading and writing in the English Renaissance. (Massachusetts studies in early modern culture.) Amherst, MA: University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 9781558490703
- Starkey, David J., and Morten Hahn-Pedersen. 2005. Bridging Troubled Waters: Conflict and Co-operation in the North Sea Region since 1550. Esbjerg: Fiskeri- og Søfartsmuseets. ISBN 8790982304
- Thernstrom, Stephan. 1980. Harvard Encyclopedia of American ethnic groups. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University. ISBN 9780674375123
- Thoen, Erik, and Leen van Molle. 2006. Rural history in the North Sea area: an overview of recent research, Middle Ages-twentieth century. (CORN publication series, 1.) Turnhout: Brepols. ISBN 9782503510057
- Tiedeke, Thorsten, and Werner Weiler. 2007. North Sea coast: landscape panoramas. Nelson: NZ Visitor. ISBN 9781877339653
- Waddington, Clive, and Kristian Pedersen. 2007. Mesolithic studies in the North Sea Basin and beyond: proceedings of a conference held at Newcastle in 2003. Oxford: Oxbow Books. ISBN 1842172247
- Wells, Peter S. 1999. The barbarians speak: how the conquered peoples shaped Roman Europe. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691089782
- Ziegler, Peter A. 1990. Geological atlas of Western and Central Europe. Shell. ISBN 9789066441255
- Zeelenberg, Sjoerd. 2005. Offshore wind energy in the North Sea Region: the state of affairs of offshore wind energy projects, national policies and economic, environmental and technological conditions in Denmark, Germany, The Netherlands, Belgium and the United Kingdom. Groningen: University of Groningen. OCLC 71640714
External links
All links retrieved November 16, 2022.
- OSPAR Commission Homepage an international commission designed to protect and conserve the North-East Atlantic and its resources
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.