A gland is an organ or a collection of cells (a tissue) in an animal's body that processes substances from the blood into a newly synthesized or concentrated chemical substance for secretion, either for use by another part of the body or for elimination from the body. The two classes of glands are endocrine glands, which synthesize a hormone for release into the bloodstream, and exocrine glands, which secrete a substance directly into cavities inside the body or onto its outer surface. More broadly, the term gland is sometimes expanded to include any collection of cells that secretes a chemical substance, such as plant glands that produce nectar in flowers.
Considered as a group, the endocrine glands make up the endocrine system, representatives of which include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas. Hormones from the endocrine glands circulate widely throughout the blood system often triggering a response in an organ or tissue far from the gland of origin. The exocrine glands secreting their products through ducts are also known as duct glands. Typical exocrine glands include sweat glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, and many glands of the digestive system.
Some glands would qualify for both groups because of their dual functions. The pancreas, for example, has both an endocrine function in releasing hormones into the bloodstream and an exocrine function in releasing digestive enzymes into the digestive tract. Other glands serving similar dual functions include the liver, ovaries, and testes.
Although the endocrine and exocrine glands considered together as a family are identified as the instruments of secretion in the animal world, they are only the larger, more obvious sources of secretions. Other sources of secretions include the heart, gut, skin, and kidneys, for example. They each secrete hormones into the blood that travel an often-long distance before interacting with a cell to the extent of affecting which genes are converted into proteins. The glands and all other sources of secretions, being part of a single organism, are nurtured by the same blood, which is maintained by the whole organism as it moves, breaths, eats, digests, eliminates, and sleeps depending on the balanced functioning of all its glands. In this we see reflected the interdependent relations characteristic of both living and social systems.
Formation
During an organism's embryonic development, its glands are formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may from the beginning possess a tubular structure, or, in other instances, it may start as a solid column of cells that subsequently becomes tubulated.
As growth proceeds, the column of cells may divide or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited; in others (salivary, pancreas), a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. In compound glands, the secretory epithelium forms the terminal portion of each branch, and the uniting portions form ducts and are lined with a less modified type of epithelial cell.
Glands are classified according to their shape.
- If the gland retains its shape as a tube throughout it is termed a tubular gland.
- In the second main variety of gland, the secretory portion is enlarged and the lumen variously increased in size. These are termed alveolar or saccular glands.
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands secrete their product directly onto a surface rather than through a duct. The human body contains several endocrine glands and cells that secrete hormones that carry out certain functions. The main glands in humans are the pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, and the reproductive glands (ovaries in women and testes in men).
Endocrine glands make up part of the endocrine system, which also includes hormones, and target cells as the three main elements.
Other organs of the body also produce and secrete hormones, but are generally not considered part of the endocrine system; these include the heart, kidney, liver, thymus, skin, and placenta. Sometimes the thymus gland and the kidney are included as part of the endocrine system, and the pineal gland sometimes is not included.
Greater detail on endocrine glands can be assessed here and a list of endocrine glands is available here.
Exocrine glands
Exocrine glands release their secretions through ducts into the external environment (Silverthorn 2004), or directly onto the exterior surface or an area contiguous with the exterior surface, not utilizing the blood to deliver the product. They include such glands as the salivary glands, sweat glands, and glands within the gastrointestinal tract. Most utilize ducts, but some glands classified as exocrine glands, such as the digestive glands in the intestine and the sebaceous glands of the skin, actually open directly onto the body surface.
The chemical substances released by exocrine glands include sweat, digestive enzymes, tears (through tear ducts), and even silk from spiders or silkworm larvae.
There are multiple ways of classifying exocrine glands:
Structure. Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland.
- The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called simple).
- The glandular portion may be tubular, acinar, or may be a mix of the two (called tubuloacinar). If the glandular portion branches, then the gland is called a branched gland.
Method of secretion. Exocrine glands are named apocrine, holocrine, or merocrine glands based on how their product is secreted.
- Apocrine glands. In apocrine glands, a portion of the plasma membrane buds off the cell, containing the secretion, such that a portion of the secreting cell's body is lost during secretion. Apocrine gland is often used to refer to the apocrine sweat glands, however it is thought that apocrine sweat glands may not be true apocrine glands as they may not use the apocrine method of secretion.
- Holocrine glands. In holocrine glands, the entire cell disintegrates to secrete its substance (e.g., sebaceous glands).
- Merocrine glands. In merocrine glands, cells secrete their substances by exocytosis (e.g., mucous and serous glands). Also called "eccrine."
Product secreted
- Serous glands. Serous glands secrete a watery, often protein-rich and often enzymes. Examples include chief cells and Paneth cells.
- Mucous glands. Mucous glands secrete a viscous product, rich in carbohydrates (eg. glycoproteins). Examples include Brunner's glands, esophageal glands, and pyloric glands.
- Mixed glands. Mixed glands secrete both protein and mucus. Examples include the salivary glands, although parotid gland is predominantly serous, and sublingual gland is predominantly mucous.
- Sebaceous glands. Sebaceous glands secrete a lipid product.
Types of exocrine glands
Glands typically may be referred to by two or more means, though some terms are rarely seen. The names of the anatomists who first described them are often employed.
| name(s) | location | product | structure |
| apocrine sweat glands | skin | - | coiled tubular |
| Bartholin's glands, Tiedmann's glands, vulvovaginal glands | vulva, vagina | - | - |
| Baughin's glands, anterior lingual glands | tongue, near tip | nonserious or mixed | - |
| Brunner's glands, duodenal glands | duodenum | mucous | compound tubular |
| bulbourethral glands, Cowper's glands, Mery's glands | penis, base | - | - |
| Ciaccio's glands, accessory lacrimal glands | eye | - | - |
| Cobelli's glands | esophagus, just above the cardia, in the mucosa | mucous | - |
| Duverney's gland | vagina, on either side | - | - |
| Ebner's glands | tongue | mucous | - |
| eccrine sweat glands | skin | - | coiled tubular |
| esophageal glands | esophagus | mucous | racemose |
| exocrine pancreas | pancreas | serous | tubulo-acinar |
| Fränkel's glands | vocal cords, below the edge | - | - |
| gastric chief cell, Wasmann's glands | stomach | serous | - |
| glomus coccygeum, coccygeal gland, Luschka's gland or ganglion | coccyx, near the tip | - | - |
| goblet cells | digestive tract, respiratory tract | mucous | simple unicellular |
| Henle's glands | eyelids, in the conjuctiva | - | tubular |
| Huguier's glands | vagina | - | - |
| Krause's glands | conjunctiva, middle portion | mucous | - |
| Lieberkuhn's glands | intestines, surface of mucous membrane | - | simple tubular |
| Littré's glands, Morgagni's glands | spongy portion of the urethra | - | racemose |
| mammary gland | breast | - | compound tubulo-acinar |
| Meibomian gland | eyelids | sebaceous | - |
| Moll's glands | eyelids | - | - |
| Montgomery's glands | mammary areola | sebaceous | - |
| Naboth's glands | cervix and os uteri | mucous | - |
| olfactory glands, Bowman's glands | nose, olfactory region | - | - |
| Paneth cells | small intestine | serous | - |
| parathyroid glands, Gley's glands, Sandstroem's glands | thyroid, on surface | - | - |
| parotid gland | mouth | serous | tubulo-alveolar |
| Peyer's patches (or glands) | ileum, lymphatic glands | - | - |
| pyloric glands | stomach | mucous | simple branched tubular |
| sebaceous gland | skin | sebum | acinar - branched |
| Skene's glands, Guérin's glands | vagina | - | - |
| sublingual gland, Rivini's gland | mouth | mucus (primarily) | tubulo-alveolar |
| submandibular gland | mouth | mixed (M+S) | tubulo-alveolar |
| sudoriparous glands, Boerhaave's glands | skin | - | - |
| Sigmund's glands | epitrochlear lymph nodes | - | - |
| Suzanne's gland | mouth, beneath the alveolingual groove | mucous | - |
| Weber's glands | tongue | mucous | tubular |
| Glands of Zeis | eyelids, free edges | sebaceous | - |
Additional images
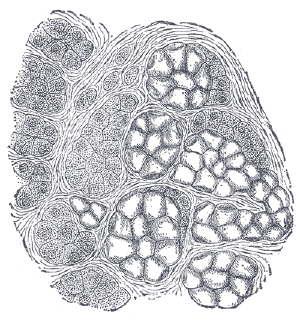
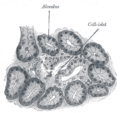
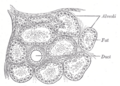
Section of pancreas of dog. X 250.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- This article incorporates text from the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, a publication now in the public domain.
- Howat, H. T., and H. Sarles. The Exocrine Pancreas. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1979. ISBN 0721647790.
- Silverthorn, D. Human Physiology, An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition). San Francisco, CA: Benjamin Cummings, 2004. ISBN 0131020153.
mechanism (Merocrine, Apocrine, Holocrine) shape (Tubular gland, Alveolar gland) secretion (Serous glands, Mucous glands, Serous demilune)
Ducts: Interlobar duct, Interlobular duct, Intralobular duct (Striated duct, Intercalated duct), Acinus
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.