Kabbala (or Kabbalah) (Hebrew: קַבָּלָה, meaning "received tradition") refers to an esoteric collection of Jewish mystical doctrines about Yahweh (God) and God's relationship to Creation. Kabbalists believe that the Torah ("Divine Law") contains deeper, hidden truths, which only the spiritually developed person can decipher. The Torah is said to be couched in symbolic language with an inner meaning that reveals a blueprint for the universe, and esoteric knowledge concerning God, the human being and the relationship between them. According to Kabbalists, those people who interpret the Bible literally, only understand half truths or worse, complete falsehoods.[1]
Historically, the term Kabbalah was first used in Jewish Talmudic texts, among the Geonim (early medieval Rabbis) and by Rishonim (later medieval Rabbis) as a reference to the full body of Judaism's oral law. Over time, much of the oral law was recorded in the Mishnah; but when the Zohar was presented to the public in the thirteenth century, the term Kabbalah specifically began to refer to its mystical teachings. Eventually, different mystical Kabbalistic brotherhoods developed called the baale ha-kabbalah (בעלי הקבלה "possessors or masters of the Kabbalah"). By the Middle Ages, especially between 1500 and 1800 C.E., Kabbalah became very popular and "was widely considered to be the true Jewish theology."[2] Its popularity waned with the rise of the Age of Enlightenment and its focus on rationality over mysticism. Recently, there has been a resurgence of interest in Kabbalah in the twenty-first century, by both Jews and non-Jews alike. Jewish mysticism remains an influential stream of Jewish theology today.
History
Origins
The origins of Kabbalah are sometimes traced back to the first man in Jewish cosmology, Adam. It is said that God revealed divine secrets to Adam such as the ten emanations of creation (see below), the Godhead, the true nature of Adam and Eve, the Garden of Eden, and the Tree of Life.[3] Most claims for the origins of Kabbalah are, accordingly, based on this argument of authority based on antiquity. As a result, many Kabbalistic works pseudepigraphically claim ancient authorship.[4] This tendency toward pseudepigraphy is also found in Apocalyptic literature, which claims that esoteric knowledge such as magic, divination and astrology was transmitted to humans in the mythic past by the two angels, Aza and Azaz'el (in other places, Azaz'el and Uzaz'el) who 'fell' from heaven (see Genesis 6:4).
The actual origins of Kabbalah are obscure, resulting from the fact that the practice was, for a long time, shrouded in secrecy amidst closed circles, which restricted its study to only certain individuals, such as married men over the age of 40.[5] These restrictions were introduced to preserve the tradition’s secrets, which were considered too powerful, dangerous and overwhelming to be handled lightly. mainstream Jewish leaders also, ironically, contributed to the secretive nature of Kabbalah because some of them considered the practice to be contaminated by idolatry and therefore embarrassing to Judaism with its talk of other worlds, God forces and harnessing the powers of Creation.[6]
Formative influences
Apocalyptic literature belonging to the pre-Christian centuries contained elements that carried over to later Kabbalah. According to the historian Josephus (37-101 C.E.), secretive writings were in the possession of the Essenes, and were jealously guarded by them against disclosure [7]. Jewish forms of esotericism, therefore, existed over 2000 years ago, and Ben Sira warned against it, saying: "You shall have no business with secret things" (Sirach iii. 22; compare Talmud Hagigah 13a; Midrash Genesis Rabbah viii.). Allusions to books containing secret lore were kept hidden away by (or for) the "enlightened" were found in IV Esdras xiv. 45-46, where Pseudo-Ezra is told to publish the 24 books of the Jewish canon openly that the worthy and the unworthy may alike read, but to keep the 70 other books hidden in order to "deliver them only to such as be wise" (compare Dan. xii. 10); for in them are the spring of understanding, the fountain of wisdom, and the stream of knowledge.
Additionally, the Book of Jubilees, refers to mysterious writings of Jared, Cain, and Noah, and presents Abraham as the renewer, and Levi as the permanent guardian, of these ancient writings. It offers a cosmogony based upon the 22 letters of the Hebrew alphabet, connected with Jewish chronology and Messianology, while at the same time insisting upon the heptad (7) as the holy number rather than upon the decadic (10) system adopted by the later haggadists and the Sefer Yetzirah.
Early elements of Jewish mysticism can be found in the non-Biblical texts of the Dead Sea Scrolls, such as the Song of the Sabbath Sacrifice. Some parts of the Talmud and the midrash also focus on the esoteric, particularly Chagigah 12b-14b.
The Bible provides ample material for Kabbalistic speculation, especially the story of Ezekiel and the chariot. The prophet Ezekiel's visions attracted much mystical speculation, as did Isaiah's Temple vision. In the Book of Ezekiel, the prophet describes a surreal journey in which he envision strange things such as wheels soaring through the sky or a valley of dry bones where the skeletons shake and rattle and suddenly reconstruct themselves into flesh-and-blood.[8] Most importantly, the story of Ezekiel’s encounter with God describes how the heavens open up and he sees four-faced figures emerge from a cloud of flashing fire: a man, a lion, an ox, and an eagle. Beneath their cloven feet, Ezekiel sees four wheels that move in conjunction with the figures, and he realizes the spirit of the four beings resides in the wheel. Finally, above the four figures, Ezekiel sees God sitting on a chariot or throne of blue lapis. The Lord gives Ezekiel his prophecies of doom and salvation for the Jewish people. The unique nature of the Book of Ezekiel caught the attention of the Kabbalists; no other prophets had written of their meeting with God in such mystical, vivid or detailed terms.[9] Kabbalists believed that Ezekiel was recounting the realms that one passed through before hearing the voice of God. They reasoned Ezekiel knew that the age of prophecy was coming to an end and thus recorded his experiences so that future generations could continue on the same spiritual path.[10]
The Book of Ezekiel sparked much discussion on the mysteries of the heavens as the mystics pondered how they could progress on Ezekiel’s path and achieve knowledge of God and the divine world. By studying the steps that Ezekiel described, the mystics believed they too could achieve divine prophecy and that anyone with skills to reach God could find God anywhere. God was knowable and accessible through the power of human intellect, but only if they developed those powers.[11]
This was the era of early Jewish mysticism, which began sometime around the first century B.C.E. and continued for nearly a millennium. It became known as Merkavah mysticism, so-called for the Hebrew word for the chariot that Ezekiel described as God’s moving throne.[12] Other biblical sources of Kabbalah are Jacob's vision of the ladder to heaven and Moses' experience with the Burning bush and his encounters with God on Mount Sinai. These mystical events in the Tanakh inspired the growth of Jewish Kabbalah.
Talmudic period
In Talmudic times, Jewish esoteric teachings were called Ma'aseh Bereshit ("Works of Creation") and Ma'aseh Merkabah ("Works of the Divine Throne/Chariot"). They are based upon Genesis 1 and Book of Ezekiel 1:4-28; the names Sitrei Torah (Talmud Hag. 13a) and Razei Torah (Ab. vi. 1) indicate their character as secret lore. Historians generally date the start of Kabbalah as a major influence in Jewish thought and practice with the publication of the Zohar and climaxing with the spread of the Arizal's teachings. The majority of Haredi Jews accept the Zohar as the representative of the Ma'aseh Merkuva and Ma'aseh B'resheyth that are referred to in Talmudic texts.
Followers of the Merkavah tradition found a new source of ideas between the third and sixth centuries C.E. A short essay called Sefer Yetzirah, or the "Book of Creation," had emerged, laying out a theory of Creation and the order of the universe based on interpretations of the Book of Genesis[13] The ideas presented in the Book of Creation would pave the way for the future core of Kabbalist creation theory.[14]
The Book of Genesis describes the process of Creation in which God created heaven and earth and all the flora and fauna within it, ending with one human to inhabit the world – Adam. However, to Kabbalists, the suggestion that God toiled to create a universe for no particular reason seems absurd, mundane, simplistic and at the very worst, sacrilegious.[15] Early mystics focused on understanding the meaning of Creation, developing their own symbolic interpretation of it.
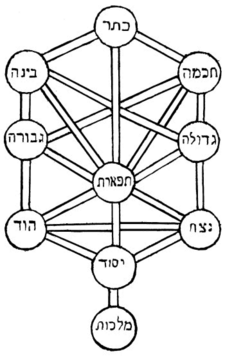
The Book of Creation interpreted Genesis on two levels: firstly, at the level of conception and secondly, at the level of physical manifestation. The Godhead first conceived the idea of creation and from that idea, His will became reality. With divine wisdom, the Godhead created ten emanations, the sefirot. These sefirot were ten elemental energy forces that were characteristics of God and agents of all Creation.[16] Creation occurred through 32 paths, a number derived from adding the ten sefirot and the 22 letters of the Hebrew alphabet. In other words, through the interaction between the letters of the alphabet and the powers of God, all Creation came into being. Thus, the 32 paths of wisdom which created the universe can be found in the Torah. The sefirot are sometimes depicted in an interconnected diagram called the Tree of Life, a main symbol for Kabbalah (see figure above).
From the eighth-eleventh centuries, Sefer Yetzirah and Hekalot texts made their way into European Jewish circles. Modern scholars have identified several mystical brotherhoods that functioned in Europe starting in the twelfth century. Some, such as the "Iyyun Circle" and the "Unique Cherub Circle," were truly esoteric, remaining largely anonymous. One well-known group was the "Hasidei Ashkenaz." This thirteenth century movement arose mostly among a single scholarly family, the Kalonymus family of the French and German Rhineland. There were certain rishonim ("Elder Sages") of exoteric Judaism who are known to have been experts in Kabbalah. One of the best known is Nahmanides (the Ramban) (1194-1270) whose commentary on the Torah is considered to be based on Kabbalistic knowledge as well as Bahya ben Asher (the Rabbeinu Behaye) (d. 1340). Another was Isaac the Blind (1160-1235), the teacher of Nahmanides, who is widely argued to have written the first work of classic Kabbalah, the Bahir (see below).
The Sefer Bahir and another work entitled "Treatise of the Left Emanation," probably composed in Spain by Isaac ben Isaac ha-Cohen, laid the groundwork for the composition of Sefer Zohar, written by Moses de Leon at the end of the thirteenth century, but credited to the Talmudic sage Simeon bar Yohai, cf. Zohar. As it developed, the ideas of Kabbalah were passed down from master to disciple, remaining relatively obscure. This began to change towards the end of the thirteenth century, when the Sefer Ha Zohar or Book of Splendour, was first published. It became the seminal work of Kabbalah. The Zohar proved to be the first truly "popular" work of Kabbalah, and the most influential. From the thirteenth century onward Kabbalah began to be widely disseminated and it branched out into an extensive literature.
When the Jews were expelled from Spain in the 1492, they carried the Zohar with them to other Jewish communities in places such as North Africa, Turkey, Babylon, and Palestine.[17] In the hill town of Safed in Galilee, the Zohar had a particular impact on such notable mystics as Moses Cordovero (1522–1570) and Isaac Luria (1534 – 1572).[18]
Rabbi Isaac Luria did not focus on the world’s creation, but on its end, with the salvation of souls and the end of the millennium. The preeminent twentieth century scholar of Kabbalah, Gershom Scholem, explained Luria’s focus on redemption as a product of the times. Following their traumatic expulsion from Spain, the Jews of the sixteenth century were seeking an explanation for their persecution.[19] Luria provided his followers with an explanation by making exile the first, necessary step in a process of universal redemption. He made the concept of exile meaningful in terms of his doctrine of transmigration of souls. His teachings to his disciples became known as Lurianic Kabbalah, and form the basis of most Kabbalah teachings and writings today.[20]
Lurianic kabbalists reimagined the sefirot as ten "vessels" that, at the moment of God's creation of the world, were unable to contain the immense flow of divine energy.[21] The seven lower vessels broke, trapping divine sparks in their shards and making the world a prison for divine souls. The exiled souls could find a way to return to heaven if they could separate themselves from the darkness and evil surrounding them, just as the grain is extracted from a husk. Each soul had to experience repeated reincarnations in order to pass through the long and difficult process of purification.[22] The process of tikkun aims to free all the divine sparks to rejoin God and restore the original whole. Lurianic kabbalah teaches that everyone plays a role in this redemption, since every good act on earth releases a divine spark.[23]
Luria thus tried to explain to the Jews the reason for their suffering as well as offer them a more optimistic vision of a time when every soul would return from exile and rejoice in the millennium. Humans were responsible for their own sin and their suffering, due to their sins in previous existences. However, God was compassionate and offered each soul the chance to repent, to seek purification and to find redemption.
After years of being persecuted, exiled and murdered across the countries of Europe, the Jewish people found spiritual succor in the teachings of Kabbalah.[24] Lurianic Kabbalah offered Jews signs that the world was indeed starting to reach the final stages of redemption, and sparked a Messianic fervor within the population.[25] The period in which the teachings of Luria dominated represented the golden era of Kabbalah studies.[26] In the seventeenth century, Lurianic Kabbalah spread from Persia to North Africa to Italy and Eastern Europe. People regarded the Kabbalah highly and the mystical tradition formed a major part of Jewish studies and teachings in the Middle East and in most of Europe. In that time, the revealed and hidden Torah were embraced equally and a unified Jewish theology existed.[27]
Following the upheavals and dislocations in the Jewish world as a result of the Spanish Inquisition and the expulsion of the Jews from Spain in 1492, the trauma of Anti-Semitism during the Middle Ages, Jews began to search for signs of when the long-awaited Jewish Messiah would come to comfort them in their painful exiles. Moses Cordovero and his immediate circle popularized the teachings of the Zohar which had until then been only a modestly influential work. The author of the Shulkhan Arukh (the Jewish "Code of Law"), Rabbi Yosef Karo (1488-1575), was also a great scholar of Kabbalah and spread its teachings during this era. As part of that "search for meaning" in their lives, Kabbala received its biggest boost in the Jewish world with the explication of the Kabbalistic teachings of Rabbi Isaac Luria (1534-1572) by his disciples Rabbi Hayim Vital and Rabbi Israel Sarug, both of whom published Luria's teachings (in variant forms) gaining them wide-spread popularity. Luria's teachings came to rival the influence of the Zohar and Luria stands, alongside Moses De Leon, as the most influential mystic in Jewish history.
The Kabbala of the Sefardi (Spanish/Mediterranean) and Mizrahi (African/Asian) Torah scholars has a long history. Kabbalah flourished among Sefardic Jews in Tzfat (Safed), Israel even before the arrival of Isaac Luria, its most famous resident. The great Yosef Karo, author of the Shulchan Arukh was part of the Tzfat school of Kabbalah. Shlomo Alkabetz, author of the famous L'cha Dodi, taught there. His disciple Moses ben Jacob Cordovero authored Sefer Pardes Rimonim, an organized, exhaustive compilation of kabbalistic teachings on a variety of subjects up to that point. Rabbi Cordovero headed the Academy of Tzfat until his death, when Isaac Luria, also known as the Ari, rose to prominence. Rabbi Moshe's disciple Eliyahu De Vidas authored the classic work, Reishit Chochma, combining kabbalistic and mussar teachings. Chaim Vital also studied under Rabbi Cordovero, but with the arrival of Rabbi Luria became his main disciple. Vital claimed to be the only one authorized to transmit the Ari's teachings, though other disciples also published books presenting Luria's teachings.
Kabbalah in various forms was widely studied, commented upon, and expanded by North African, Turkish, Yemenite, and Asian scholars from the sixteenth century onward. Among the most famous was the "Beit El" mystical circle of Jerusalem, originally a brotherhood of 12, mostly Sefardic, mystics under the leadership of Gedaliyah Chayon and Shalom Sharabi in the mid-eighteenth century. The group endured into the twentieth century.
One of the most important teachers of Kabbalah recognized as an authority by all serious scholars up until the present time, was Rabbi Judah Loew ben Bezalel (1525-1609) known as the Maharal of Prague. Many of his written works survive and are studied for their deep Kabbalistic insights. The Maharal is, perhaps, most famous outside of Jewish mysticism for the legends of the golem of Prague, which he reportedly created. During the twentieth century, Rabbi Isaac Hutner (1906-1980) continued to spread the Maharal's teachings indirectly through his own teachings and scholarly publications within the modern yeshiva world.
The spiritual and mystical yearnings of many Jews remained frustrated after the death of Rabbi Isaac Luria and his disciples and colleagues. No hope was in sight for many following the devastation and pogroms that followed in the wake the Chmielnicki Uprising (1648-1654), and it was at this time that a controversial scholar of the Kabbalah by the name of Sabbatai Zevi (1626-1676) captured the hearts and minds of the Jewish masses of that time with the promise of a newly-minted "Messianic" Millennialism in the form of his own personage. His charisma, mystical teachings that included repeated pronunciations of the holy Tetragrammaton in public, tied to an unstable personality, and with the help of his own "prophet" Nathan of Gaza, convinced the Jewish masses that the "Jewish Messiah" had finally come. It seemed that the esoteric teachings of Kabbalah had found their "champion" and had triumphed, but this era of Jewish history unravelled when Zevi became an apostate to Judaism by converting to Islam after he was arrested by the Ottoman Sultan and threatened with execution for attempting a plan to conquer the world and rebuild the Temple of Jerusalem.
Many of his followers continued to worship him in secret, explaining his conversion not as an effort to save his life but to recover the sparks of the holy in each religion, and most leading rabbis were always on guard to root them out. The "Donmeh" movement in modern Turkey is a surviving remnant of the Sabbatian schism. The Sabbatian movement was followed by that of the "Frankists" who were disciples of another pseudo-mystic Jacob Frank (1726-1791) who eventually became an apostate to Judaism by apparently converting to Catholicism. This era of disappointment did not stem the Jewish masses' yearnings for "mystical" leadership.
Modern period
The eighteenth century saw an explosion of new efforts in the spread of Kabbalah by four well known rabbis working in different areas of Europe:
- Rabbi Israel ben Eliezer (1698-1760) in the area of Ukraine spread teachings based on Rabbi Isaac Luria's foundations, simplifying the Kabbalah for the common person. From him, sprang the vast ongoing schools of Hasidic Judaism, with each successive rebbe viewed by his "Hasidim" as continuing the role of dispenser of mystical divine blessings and guidance.
- Rebbe Nachman of Breslov (1772 - 1810), the great-grandson of the Baal Shem Tov, revitalized and further expanded the latter's teachings, amassing a following of thousands in Ukraine, White Russia, Lithuania and Poland. In a unique amalgam of Hasidic and Mitnagid approaches, Rebbe Nachman emphasized study of both Kabbalah and serious Torah scholarship to his disciples. His teachings also differed from the way other Hasidic groups were developing, as he rejected the idea of hereditary Hasidic dynasties and taught that each Hasid must "search for the tzaddik ('saintly/righteous person')" for himself—and within himself.
- Rabbi Elijah of Vilna (Vilna Gaon) (1720-1797), based in Lithuania, had his teachings encoded and publicized by his disciples such as by Rabbi Chaim Volozhin who published the mystical-ethical work Nefesh HaChaim. However, he was staunchly opposed to the new Hasidic movement and warned against their public displays of religious fervor inspired by the mystical teachings of their rabbis. Although the Vilna Gaon was not in favor of the Hasidic movement, he did not prohibit the study and engagement in the Kabbalah. This is evident from his writings in the Even Shlema. "He that is able to understand secrets of the Torah and does not try to understand them will be judged harshly, may God have mercy." (The Vilna Gaon, Even Shlema, 8:24). "The Redemption will only come about through learning Torah, and the essence of the Redemption depends upon learning Kabbalah" (The Vilna Gaon, Even Shlema, 11:3).
- Rabbi Moshe Chaim Luzzatto (1707-1746), based in Italy, was a precocious Talmudic scholar who arrived at the startling conclusion that there was a need for the public teaching and study of Kabbalah. He established a yeshiva (a Rabbinic academy) for Kabbalah study and actively recruited outstanding students. Additionally, he wrote copious manuscripts in an appealing clear Hebrew style, all of which gained the attention of both admirers as well of rabbinical critics who feared another "Zevi (false messiah) in the making." He was forced to close his school by his rabbinical opponents, hand over and destroy many of his most precious unpublished kabbalistic writings, and go into exile in the Netherlands. He eventually moved to the Land of Israel. Some of his most important works such as Derekh Hashem survive and are used as a gateway to the world of Jewish mysticism.
Two of the most influential sources spreading Kabbalistic teachings have come from the growth of Hasidic Judaism, as can be seen by the Lubavitch movement, and from the influence of the writings of Rabbi Abraham Isaac Kook (1864-1935) who inspired the followers of Religious Zionism with mystical writings and the hope Zionism would bring on the "beginning of the redemption" of the Jewish people from their exile. The varied Hasidic works (sifrei chasidus) and Rabbi Kook's voluminous writings drew heavily on the long chain of Kabbalistic thought and methodology.
Another influential and important Kabbalah character is Rabbi Yehuda Leib Ashlag (1884-1954) (also known as the Baal HaSulam—a title that he was given after the completion of one of his masterworks, The Sulam). Ashlag is considered by many to be one of the greatest Kabbalists of all time. He developed a study method that he considered most fitting for the future generations of Kabbalists. He is also notable for his other masterwork Talmud Eser HaSfirot—The Study of the Ten Emanations—a commentary on all the writings of the ARI. Some today consider this work as the core of the entire teaching of Kabbalah. Baal Hasulam's goal was to make the study of Kabblah understandable and accessible to every human being with the desire to know the meaning of life.
During the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, Kabbalah’s influence in mainstream Judaism weakened. However, Jewish Hassidim, which was influenced by Lurianic Kabbalah and the idea of divine sparks, kept the Kabbalistic teachings alive.[28] In recent years, renewed interest in Kabbalah has appeared among non-traditional Jews, and even among non-Jews. Neo-Hasidism and Jewish Renewal have been the most influential groups in this trend.
Now, in the last twenty years, Kabbalah has made a powerful reemergence. Jews, non-Jews and even celebrities are rediscovering the Kabbalah’s mystical meanings and trying to apply them to the modern times. By understanding the unity of existence and the divinity manifest in everything, kabbalist seekers aim to bring balance and harmony to the universe.[29]
Teachings
The Emanation of En Sof
Kabbalists understand the profound source of everything to be the supreme, eternal and unchanging Godhead, which they called En Sof or “no end”[30] The Kabbalists regarded En Sof as a divine realm beyond all description, which could not even be given a symbol based on the scriptures, as the Bible never directly mentioned it. To call it “no end” was to refer to something beyond human language.
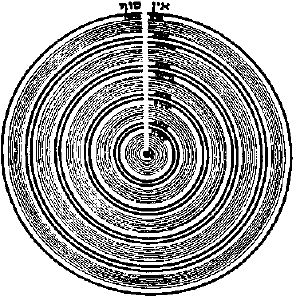
The Kabbalists understood that in the beginning, there was only En Sof, an infinite white ray of light of infinite intensity, singular unity and oneness. The En Sof willed itself to withdraw from Itself to make a space for Creation to exist within, which is represented by the first sefira, Keter. This contraction of space is seen to address the paradox of an imperfect, finite world existing within the absolute perfection and unity of the Godhead.[31] When Creation occurred, the infinite ray of light entered the contracted space and thus, the En Sof breathed life into the emptiness.[32] The Godhead sent out a stream of pure, white light into the darkness, an emanation of his energy which is represented by the second sefira, the Hochma. While the white light remained connected to En Sof, it began to reach further and further. Ten concentric spheres of diminishing light emerged in the original darkness, all together representing the ten Sefirot. Somewhere on top of their common centre lies the point of infinity.
Kabbalists saw the secret of creation, or sod ma’aseh bereshit, as a divine ladder where the emanation led away from the original unity of God. In the resulting plurality of the physical world, everything is separate and unable to be united with one other. The mystic longs to turn away from this plurality and become reunited with the true divine. The mystic tries to ascend the ladder and relive the creation process from end to beginning to uplift the soul towards the sublime unity.
Creation (through the Sefirot)
In the first chapter of the Torah, Genesis, the world is created in the ten utterances of God. Each of these divine surges of energy are what lie behind all reality, according to Kabbalists. Everything in the world can be referred back to the Torah, because the world was created through the Torah.[33]For kabbalists the ten utterances are linked to the ten sefirot, which is the divine structure of all being.[33]
According to Kabbalistic cosmology, Ten Sefirot (literally, "Ten Numerations") correspond to ten levels of creation, which are ten different ways of revealing God. It is not God who changes but the ability to perceive God that changes. While God may seem to exhibit dual natures (masculine-feminine, compassionate-judgmental, creator-creation), all adherents of Kabbalah have consistently stressed the ultimate unity of God. For example, in all discussions of Male and Female, the hidden nature of God exists above duality without limit, being called the Infinite or the "No End" (Ein Sof). Hiddenness makes creation possible because God can then become "revealed" in a diversity of limited ways, which then form the building blocks of creation. The Ten Sefirot mediate the interaction of the ultimate unknowable God with the physical and spiritual world.
Kabbalists believe the universe is composed of four worlds, which are four levels of Creation. The first world is the world of emanation, which is closest to En Sof. The second is the world of creation, in which the emanations of God began to emerge as opposing, balanced forces. The third world is the one of formation, in which the interaction between the sefirot and En Sof makes everything take on shape. Finally, Assiyah is the world in which all activity becomes manifest in the physical world.
Symbolic language and number-word mysticism
Kabbalah attempts to understand the symbolic meaning of the Torah using a variety of techniques including numerology (e.g. See Gematria). The Kabbalists noted that when they examined the first sentence of Book of Genesis in Hebrew, which states “In the beginning, God created the heavens and the earth” (in Hebrew: "Bereshit bara Elohim ve et ha shamaim ve et ha aretz"), scholars realized the first letter of the Torah is bet, the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet. The Kabbalists questioned why the story of Creation and the beginning of the world did not lead off with the beginning of the alphabet?[34] They came to believe the first letter of the alphabet, aleph, does not begin the book of Genesis because it represents what came before Creation. Thus aleph becomes a symbol for the hidden Godhead, from which creation and the sefirot, or bet, flowed. Kabbalists also noticed that the word “bara, or “created” came before the name for God, Elohim. Typically, the actor comes before the word, so to say, “God created.” But in this case, Elohim becomes the object of creation and the subject of the sentence is understood as the third person singular of the verb bara (“It”). Therefore, the first part of the line reads, “In the beginning, God created God.” Since God must be the source of all things and has no creator, an alternative explanation was required.[35]
Kabbalists realized that Elohim was only one manifestation of God and that God also created other qualities of Himself to act as agents of Creation, or the sefirot. With some further interpretation, Kabbalists uncovered a new meaning of the statement “In the beginning, God created heaven and earth.” Rather, they understood that in the beginning, with divine wisdom, En Sof (which is never directly mentioned) created the sefirot and the alphabet of heaven and the alphabet of earth.[36]
Through this type of detailed analysis, the frame-work of Kabbalah emerged.
As early as the first century B.C.E., Jews believed that the Torah contained encoded message and hidden meanings. Gematria is one method for discovering the alleged hidden meanings in Torah. Each letter in Hebrew also represents a number - Hebrew, unlike many other languages, never developed a separate numerical alphabet. By converting letters to numbers, Kabbalists were able to find hidden meaning in each word. This method of interpretation was used extensively by various schools. An example would be the teachings of Rabbi Isaac Luria.
There is no one fixed way to "do" gematria because there are a "number of variations in the gematria method of decoding the Torah."[37] One such procedure is that each syllable and/or letter forming a word has a characteristic numeric value. The sum of these numeric tags is the word's "key," and that word may be replaced in the text by any other word having the same key. Through the application of many such procedures, alternate or hidden meanings of scripture may be derived. Similar procedures are used by Islamic mystics, as described by Idries Shah in his book, The Sufis.[38]
The Nature of God
Kabbalah teaches that God is neither matter nor spirit. Rather God is the creator of both, but is himself neither. However, if God is so different from his creation; then how can there be any interaction between the Creator and the created? This question prompted Kabbalists to envision two aspects of God, (a) the Godhead itself, who in the end is unknowable, and (b) the revealed aspect of God that created the universe, preserves the universe, and interacts with mankind. Kabbalists speak of the first aspect of God as Ein Sof (אין סוף), "the infinite," "endless." In this view, nothing can be said about this aspect of God. This aspect of God is impersonal. The second aspect of divine emanations, however, is at least partially accessible to human thought. Kabbalists believe that these two aspects are not contradictory but, through the mechanism of progressive emanation, complement one another. The structure of these emanations have been characterized in various ways: Four "worlds" (Azilut, Yitzirah, Beriyah, and Asiyah), Sefirot, or Partzufim ("faces"). Later systems harmonize these models.
Some Kabbalistic scholars, such as Moses ben Jacob Cordovero, believe that all things are linked to God through these emanations, making us all part of one great chain of being. Others, such as Schneur Zalman of Liadi (founder of Lubavitch (Chabad) Hasidism), hold that God is all that really exists; all else is completely undifferentiated from God's perspective. If improperly explained, such views can interpreted as panentheism or pantheism. However, according to this philosophy, God's existence is higher than anything that this world can express, yet, the Godhead includes all things of this world down to the finest detail in such a perfect unity that His creation of the world effected no change in Him whatsoever. This paradox is dealt with at length in the Chabad Chassidic texts.
Even in very early times of the Land of Israel as well as Alexandrian theology recognized the two attributes of God, middat hadin (the "attribute of justice"), and middat ha-rahamim (the "attribute of mercy") (Midrash Sifre, Deuteronomy 27); and so is the contrast between justice and mercy a fundamental doctrine of the Kabbalah. Other hypostasizations are represented by the ten "agencies" (the Sefirot) through which God created the world; namely, wisdom, insight, cognition, strength, power, inexorableness, justice, right, love, and mercy.
In dwelling upon the nature of God and the universe, the mystics of the Talmudic period asserted, in contrast to the transcendentalism evident in some parts of the Bible, that "God is the dwelling-place of the universe; but the universe is not the dwelling-place of God." Possibly the designation ("place") for God, so frequently found in Talmudic-Midrashic literature, is due to this conception, just as Philo, in commenting on Genesis 28:11 says, "God is called ha makom (המקום "the place") because God encloses the universe, but is Himself not enclosed by anything" (De Somniis, i. 11). This type of theology, in modern terms, is known as panentheism. The mystics also latched on to the phrase from Isaiah, as expounded by the Rabbinic Sages, "The whole world is filled with his glory," to justify a panentheistic understanding of the universe. In the seventeenth century, Baruch Spinoza may have had this passage in mind when he said that the ancient Jews did not separate God from the world. This conception of God may be pantheistic or panentheistic. It also postulates the union of man with God; both these ideas were further developed in the later Kabbalah. (Spinoza was excommunicated from the main Jewish community by the rabbis at the time for publicly espousing these views, more likely out of fear of Christian reaction then out of their own outrage).
The human soul
The Zohar posits that the human soul has three elements, the nefesh, ru'ach, and neshamah. The nefesh is found in all humans, and enters the physical body at birth. It is the source of one's physical and psychological nature. The next two parts of the soul are not implanted at birth, but can be developed over time; their development depends on the actions and beliefs of the individual. They are said to only fully exist in people awakened spiritually. A common way of explaining the three parts of the soul is as follows:
- Nefesh (נפש) - the lower part, or "animal part," of the soul. It is linked to instincts and bodily cravings.
- Ruach (רוח) - the middle soul, the "spirit." It contains the moral virtues and the ability to distinguish between good and evil.
- Neshamah (נשמה) - the higher soul, or "super-soul." This separates man from all other lifeforms. It is related to the intellect, and allows man to enjoy and benefit from the afterlife. This part of the soul is provided both to Jew and non-Jew alike at birth. It allows one to have some awareness of the existence and presence of God.
The Raaya Meheimna, a section of related teachings spread throughout the Zohar, discusses the two other parts of the human soul, the chayyah and yehidah (first mentioned in the Midrash Rabbah). Gershom Scholem writes that these "were considered to represent the sublimest levels of intuitive cognition, and to be within the grasp of only a few chosen individuals." The Chayyah and the Yechidah do not enter into the body like the other three - thus they received less attention in other sections of the Zohar.
- Chayyah (חיה) - The part of the soul that allows one to have an awareness of the divine life force itself.
- Yehidah (יחידה) - the highest plane of the soul, in which one can achieve as full a union with God as is possible.
Both rabbinic and kabbalistic works posit that there are also a few additional, non-permanent states to the soul that people can develop on certain occasions. These extra souls, or extra states of the soul, play no part in any afterlife scheme, but are mentioned for completeness:
- Ruach HaKodesh (רוח הקודש) - ("spirit of holiness") a state of the soul that makes prophecy possible. Since the age of classical prophecy passed, no one (outside of Israel) receives the soul of prophesy any longer. See the teachings of Abraham Abulafia for differing views of this matter.
- Neshamah Yeseira - The "supplemental soul" that a Jew can experience on Shabbat. It makes possible an enhanced spiritual enjoyment of the day. This exists only when one is observing Shabbat; it can be lost and gained depending on one's observance.
- Neshamah Kedosha - Provided to Jews at the age of maturity (13 for boys, 12 for girls), and is related to the study and fulfillment of the Torah commandments. It exists only when one studies and follows Torah; it can be lost and gained depending on one's study and observance.
Among its many pre-occupations, Kabbalah teaches that every Hebrew letter, word, number, even the accent on words of the Hebrew Bible contains a hidden sense; and it teaches the methods of interpretation for ascertaining these meanings.
Moreover in Kabbalah, Divine Light is the carrier of consciousness.
- "The human soul is a part of the Creator [that is, Divine Light]. Therefore, there is no difference between Him and the soul. The difference is that He is the 'whole' and the soul is a 'part'. This resembles a stone carved from a rock. There is no difference between the stone and the rock except that the rock is a 'whole' and the stone is a 'part'." (Yhuda Ashlag, Introduction in Ha-Sulam.)
Theodicy
Kabbalistic works offer a theodicy, a philosophical reconciliation of how the existence of a good and powerful God is compatible with the existence of evil in the world. According to the Kabbalah, there are mainly two different ways to describe why there is evil in the world, and both make use of the kabbalistic Tree of Life:
- The kabbalistic tree, which consists of ten Sephiroth, ("emanations" of God), consists of three "pillars": The left side of the tree, the "female side," is considered to be more destructive than the right side, the "male side." Gevurah (גבורה, "Power"), for example, stands for strength and discipline, while her male counterpart, Chesed (חסד, "Mercy"), stands for love and mercy. The "center pillar" of the tree does not have any polarity, and no gender is given to it. Thus, evil is really an emanation of Divinity, a harsh byproduct of the "left side" of creation.
- In the medieval era, this notion took on increasingly gnostic overtones. The Qliphoth (or Kelippot) (קליפות, the primeval "husks" of impurity) emanating from the left side were blamed for all the evil in the world. Qliphoth are the Sephiroth out of balance. The tree of Qliphoth is usually called the kabbalistic Tree of Death, and sometimes the qliphoth are called the "death angels," or "angels of death."[39]
- Not all Kabbalists accepted this notion of evil being in such intimate relationship with God. Moses Cordovero (sixteenth century) and Menassseh ben Israel (seventeenth century) are two examples of Kabbalists who claimed "No evil emanates from God." They located evil as a byproduct of human freedom, an idea also found in mythic form in Rabbinic traditions that claim most demons are either the "dead of the flood" or products of human sexual incontinence.
Primary Texts
Kabbalah is an ongoing oral tradition. Its texts are mostly meaningless to readers who are unfamiliar with Jewish spirituality, and assume extensive knowledge of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible), Midrash (Jewish hermeneutic tradition) and Halakha (practical Jewish law). Nevertheless, Kabbalistic literature uses powerful paradigms that are elegant, universal, and easy for anyone to understand when pointed out.
A list of the most significant Kabbalistic texts are provided below in the chronological order of their publication:
Heichalot
Hekhalot ("Heavenly Palaces") are not a single text. Rather, they are a genre of writings with shared characteristics. These texts primarily focus either on how to achieve a heavenly ascent through the Heichalot (heavenly palaces) and what to expect there, or on drawing down angelic spirits to interact and help the adept. There are several larger documents of the heichalot, such as Hekhalot Rabbati, Hekhalot Zutarti, and sixth-century 3 Khanokh, as well as hundreds of small documents, many little more than fragments.
Sefer Yetzirah
Yetzira (יצירה) (" Book [of] Formation/Creation"), also known as Hilkhot Yetzira "Customs of Formation." Its historical origins remain obscure. It exists today in a number of editions, up to 2500 words long (about the size of a pamphlet). It organizes the cosmos into "32 Paths of Wisdom," comprising "10 Sefirot" (3 elements - air, water and fire - plus 6 directions and center) and "22 letters" of the Hebrew alphabet (3 mother letters, 7 double letters plus 12 simple letters). It uses this structure to organize cosmic phenomena ranging from the seasons of the calendar to the emotions of the intellect, and is essentially an index of cosmic correspondences. The first commentaries on this small book were written in the tenth century, perhaps the text itself is quoted as early as the sixth century, and perhaps its linguistic organization of the Hebrew alphabet could be from as early as the second century.
Bahir
Bahir (בהיר) ("Illumination") (also known as "Midrash of Rabbi Nehunia Ben Ha-Kana") is a book of special interest to students of Kabbalah, about 12,000 words (about the size of a modern-day magazine). Despite its name "Illumination," it is notoriously cryptic and difficult to understand. Much of it is written in parables, one after the other. The Bahir opens with a quote attributed to Rabbi Nehunia Ben Ha-Kana, a Talmudic sage of the first century, and the rest the book is an unfolding discussion about the quote. Jewish tradition considers the whole book to be written in the spirit of Rabbi Nehunia (or even literally written by him). It was first published in Provence, France (near Italy) in 1176. Historians suspect Rabbi Yitzhak Ha-Ivver (also known as Isaac the Blind) wrote the book at this time, albeit he incorporated oral traditions from a much earlier time about the Tanakh, Talmud, Siddur, Yetzira, and other Rabbinic texts.
Sefer Chasidim
Sefer Chasidim ("Book [of] Pious Ones") arose in the late twelfth century as a central ethical text of the German Pietists. It is anonymous but sometimes credited to Shmuel Ben Yhuda He-Chasid. The text resembles a FAQ with about 1200 frequently asked questions whose answers range from exhortations to illustrative stories to homilies, about any aspect of Medieval Ashkenazi Judaism. The bulk of the book is devoted to a severe but readily understood pietism for those volunteering to do halakha above and beyond the basic duties. Some material, however, concerns Jewish mysticism: the divine economy, secrets of prayer, and paranormal phenomena such as divinatory dreams, witches, vampires, and poltergeists.
Sefer Raziel HaMalakh
Raziel Ha-Malakh (רזיאל המלאך ) ("Raziel the Angel") is an astral-magical text published in the thirteenth century in Germany and probably written by Eliezer of Worms. It cites the text of the Yetzira, explains the concept of mazal "fortune, destinity" associated with Kabbalah astrology, and records an encrypted alphabet for use in mystical formulas.
The Zohar (Book of Splendor)
Other than the Torah, the most important text of Kabbalah is the Zohar ( זהר ) ("Splendor"), at times achieving even canonical status as part of Oral Torah. It is a mystical commentary on the Torah, written in Medieval Aramaic. Most traditional Kabbalists agree that the oral author of the Zohar was Rabbi Shimon bar Yochai and the text was scribed by Rav Abba, a student of Rabbi Shimon bar Yochai. The academic opinion, however, is that Rabbi Moshe de Leon wrote it himself (or perhaps with help) before he published it in Spain in the thirteenth century.[40] He claimed to discover the text of the Zohar while in the land of Israel and attributed it to the second-century Rabbi Shimon bar Yohai who is the main character of the text. The text gained enormous popularity throughout the Jewish world. While organized into commentaries on sections of the Torah, the Zohar elaborates on the Talmud, Midrash Rabba, Yetzira, the Bahir, and many other Rabbinic texts. Though the book was widely accepted, a small number of significant rabbis over the subsequent centuries have published texts declaring Rabbi Moshe invented it as a forgery with concepts contrary to Judaism. However, many of these Rabbis were not Kabbalists themselves. This was a major point of contention made by a community among the Jews of Yemen, known as Dor Daim (a religious intellectual movement that called for a return to a more Talmudic based Judaism).
The Zohar contains a medley of ideas, fact and fiction, of history and tradition, of words, letters and stories; it moves from delicate poetry and expressions of pure thought to passages of absurd babble or streams of consciousness. It is suggested that the structure of the Zohar is only the cloak for its inner, mystical meaning[41].
The Book tells its own story of how it came to be. It says that the Rabbi Simeon ben Yohai and his son, Rabbi Eliezer, hid themselves in a cave to escape Roman persecution in Judea during the second century. In more than a decade of hiding, they wrote down their contemplations on the essence of God, the Torah, Israel and the secrets of the universe. Over time, their reflections were lost and hidden amid the treasures of the Holy Land. However, years later, a storm blew the pages into the home of the Spanish rabbi and mystic, Moses de Leon. He collected the pages and published them under the title “The Book of Splendor.”
In the Zohar, Kabbalistic ideas which were in their nascent stages blossomed and became interlinked. The primary focus of the work is the interconnectedness of the universe and the argument that behind everything there is a purpose, not just random chaos.[42]
Pardes Rimonim ("Garden [of] Pomegranates")
Pardes Rimonim ( פרדס רימונים ) ("Garden [of] Pomegranates") - the magnum opus of Rabbi Moshe Cordovero, published in Spain in the sixteenth century and the main source of Cordoverian Kabbalah, a comprehensive interpretation of the Zohar and a friendly rival of the Lurianic interpretation. Among other important books by Rabbi Moshe Cordovero is Tomer Devora.
Etz Hayim ("Tree [of] Life")
Etz Hayim ( עץ חיים ) ("Tree [of] Life") - useful text of the teachings of Rabbi Yitzhak Luria (also known as the Ari), collected by his disciples, principally Chaim Vital (the Ari published nothing himself). It is a popular interpretation and synthesis of Lurianic Kabbalah. It was first published in Safed in the sixteenth century in a form entitled Shemona She'arim (eight gates): this arrangement is still authoritative among Sephardi and Mizrahi Kabbalists. The term Etz Hayim refers to a three-part re-arrangement published later in Poland, and used by Ashkenazim.
Sulam ("Ladder")
Sulam ( סולם ) ("Ladder"), also known as Zohar im perush Ha-Sulam ("Zohar with the Explication of the Ladder") - a translation of the Zohar into Hebrew that includes parenthetical comments. Despite being a late text by a modern Kabbalist, it is widely distributed. Rabbi Yehuda Leib Ashlag wrote and published it in Israel in 1943. In the Sulam, the text of the Zohar includes parenthetical notes that explain some of the cryptic metaphors found in the Zohar, according to the interpretive tradition of Rabbi Yitzhak Luria. Much of the Zohar remains meaningless without the Sulam, and virtually every student of Kabblah must at some point refer to it.
Talmud Eser HaSfirot
Talmud Eser HaSfirot (תלמוד עשר הספירות) ("The Study [of the] Ten Sefirot"), is a commentary on all the writings of the ARI written by Rabbi Yehuda Leib Ashlag.
Criticisms
1: Problem of Dualism: One of the most serious and sustained criticisms of Kabbalah is that it may lead away from monotheism, and instead promote dualism, the belief that there is a supernatural counterpart to God. The dualistic system holds that there is a good power versus an evil power. There are (appropriately) two primary models of Gnostic-dualistic cosmology. The first, which goes back to Zoroastrianism, believes creation is ontologically divided between good and evil forces. The second, found largely in Greco-Roman ideologies like Neo-Platonism, believes the universe knew a primoridal harmony, but that a cosmic disruption yielded a second, evil, dimension to reality. This second model influenced the cosmology of the Kabbalah.
Later Kabbalistic works, including the Zohar, appear to more strongly affirm dualism, as they ascribe all evil to a supernatural force known as the Sitra Ahra ("the other side") that emantes from God. This "left side" of divine emanation is a kind of negative mirror image of the "side of holiness" with which it was locked in combat."[43] While this evil aspect exists within the divine structure of the Sefirot, the Zohar indicates that the Sitra Ahra has no power over Ein Sof, and only exists as a necessary aspect of the creation of God to give man free choice, and that evil is the consequence of this choice - not a supernatural force opposed to God, but a reflection of the inner moral combat within mankind between the dictates of morality and the surrender to one's basic instincts.
2: Exclusionary view of Soul: Another aspect of Kabbalah that Jewish critics object to is its metaphysics of the human soul. Since the Zohar, most Kabbalistic works assume that Jewish and non-Jewish souls are fundamentally different. While all human souls emanate from God, the Zohar posits that at least part of Gentile souls emanate from the "left side" of the Sefrotic structure and that non-Jews therefore have a dark or demonic aspect to them that is absent in Jews.
Later Kabbalistic works build and elaborate on this idea. The Hasidic work, the Tanya, fuses this idea with Judah ha-Levi's medieval philosophical argument for the uniqueness of the Jewish soul in order to argue that Jews have an additional level of soul that other humans do not possess.
All this theologically-framed hostility may be a response to the demonization of Jews that developed in Western and Christian thought starting with the Patristic Fathers. By the Middle Ages, Jews were widely characterized as minions of Satan, or even devilish non-humans in their own right. Modern Judaism has rejected, or at least dismissed this outdated aspect of Kabbalah as non-relevant, as it possibly persists in only the most recondite and anti-modernist corners of the Jewish world.[44]
3: Orthodox Critique:
While a portion of Modern Orthodox Rabbis, Dor Daim, and many students of the Rambam completely reject Arizal's kabbalistic teachings, as well as deny that the Zohar is authoritative, all three of these groups completely accept the existence of the esoteric side of Torah referred to in the Talmud as Ma'aseh Merquva and Ma'aseh B'resheyth. Their disagreement is only over whether the Kabbalistic teachings promulgated today are accurate representations of those esoteric teachings to which the Talmud refers. Within the Haredi Jewish community one can find Rabbis who both sympathize with such a view, while not necessarily agreeing with it, as well as Rabbis who consider such a view absolute heresy.
The idea that there are ten divine sefirot could evolve over time into the idea that "God is One being, yet in that One being there are Ten" which opens up a debate about what the "correct beliefs" in God should be, according to Judaism.
Rabbi Saadiah Gaon teaches in his book Emunot v'Deot that Jews who believe in reincarnation have adopted a non-Jewish belief.
Maimonides (twelfth century) belittled many of the texts of the Hekalot, particularly the work Shiur Komah with its starkly anthropomorphic vision of God.
Rabbi Avraham ben haRambam, in the spirit of his father Maimonides, Rabbi Saadiah Gaon, and other predecessors, explains at length in his book Milhhamot HaShem that the Almighty is in no way literally within time or space nor physically outside time or space, since time and space simply do not apply to His Being whatsoever. This is in contrast to certain popular understandings of modern Kabbalah which teach a form of panentheism, that His 'essence' is within everything.
Rabbi Yitzchak ben Sheshet Perfet (The Rivash), 1326-1408; he stated that Kabbalah was "worse than Christianity," as it made God into ten, not just into three. The critique, however, is considered irrelevant to most kabbalists. Most followers of Kabbalah never believed this interpretation of Kabbalah. The Christian Trinity concept posits that there are three persons existing within the Godhead, one of whom literally became a human being. In contrast, the mainstream understanding of the Kabbalistic sefirot holds that they have no mind or intelligence; further, they are not addressed in prayer, and they can not become a human being. They are conduits for interaction—not persons or beings. Nonetheless, many important poskim, such as Maimonidies in his work Mishneh Torah, prohibit any use of mediators between oneself and the Creator as a form of idolatry.
Rabbi Leon Modena, a seventeenth century Venetian critic of Kabbalah, wrote that if we were to accept the Kabbalah, then the Christian trinity would indeed be compatible with Judaism, as the Trinity closely resembles the Kabbalistic doctrine of sefirot. This critique was in response to the fact that some Jews went so far as to address individual sefirot individually in some of their prayers, although this practise was far from common. This interpretation of Kabbalah in fact did occur among some European Jews in the seventeenth century.
Rabbi Yaakov Emden (1697-1776), wrote the book Mitpahhath Sfarim (Scarf/Veil of the Books) which is a detailed critique of the Zohar. He concludes that certain parts of the Zohar contain heretical teaching and therefore could not have been written by Rabbi Shimon ben Yochai. Opponents of the book claim that he wrote the book in a drunken stupor.
Rabbi Yihhyah Qafahh, an early twentieth century Yemenite Jewish leader and grandfather of Rabbi Yosef Kapach, also wrote a book entitled Milhhamoth HaShem, (Wars of the L-RD) against what he perceived as the false teachings of the Zohar and the false kabbalah of Isaac Luria. He is credited with spearheading the Dor Daim. Dor Daim continue in Rabbi Yihhyah Qafahh's view of Kabbalah into modern times.
4: Enlightenment Critique: According to Rabbi Bradley Shavit Artson (Dean of the Conservative Ziegler School of Rabbinnical Studies in the University of Judaism)[45], "many western Jews insisted that their future and their freedom required shedding what they perceived as parochial orientalism. They fashioned a Judaism that was decorous and strictly rational (according to nineteenth-century European standards), denigrating Kabbalah as backward, superstitious, and marginal."
However, in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries there has been a revival in interest in Kabbalah in all branches of liberal Judaism. The Kabbalistic twelfth century prayer Ani'im Zemirot was restored to the new Conservative Sim Shalom siddur, as was the B'rikh Shmeh passage from the Zohar, and the mystical Ushpizin service welcoming to the Sukkah the spirits of Jewish forbearers. Ani'im Zemirot and the sixteenth century mystical poem Lekha Dodi reappeared in the Reform Siddur Gates of Prayer in 1975. All Rabbinical seminaries now teach several courses in Kabbalah, and the Ziegler School of Rabbinical Studies in Los Angeles has a fulltime instructor in Kabbalah and Hasidut. Reform Rabbis like Herbert Weiner and Lawrence Kushner have renewed interest in Kabbalah among Reform Jews.
According to Artson, "Ours is an age hungry for meaning, for a sense of belonging, for holiness. In that search, we have returned to the very Kabbalah our predecessors scorned. The stone that the builders rejected has become the head cornerstone (Psalm 118:22)…. Kabbalah was the last universal theology adopted by the entire Jewish people, hence faithfulness to our commitment to positive-historical Judaism mandates a reverent receptivity to Kabbalah".[3]
Notes
- ↑ J. Dan, "Gershom Scholem’s reconstruction of early Kabbalah." Modern Judaism 5 (1985): 39–66.
- ↑ Gershom Scholem. Kabbalah. (Jewish Publication Society. ISBN 978-0880292054)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bradley Shavit Artson, [1]. "From the Periphery to the Centre: Kabbalah and the Conservative Movement," United Synagogue Review (Spring 2005) 57 (2).
- ↑ For example, Sefer Raziel HaMalach, an astro-magical text partly based on a magical manual of late antiquity, Sefer ha-Razim, was, according to the kabbalists, transmitted to Adam (after being evicted from Eden) by the angel Raziel. Another famous work, the Sefer Yetzirah, supposedly dates back to the patriarch Abraham.
- ↑ Dan, 1985; K. Zetter. Simple Kabbalah. (Berkeley: Conari Press. ISBN 978-0785815112).
- ↑ M. Goldish, "Kabbalah, academia, and authenticity." Tikkun 20 (2005): 63-67; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ see Philo, "De Vita Contemplativa," iii.; and Hippolytus, "Refutation of all Heresies," ix. 27)
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ J. Minkin, "Jewish mysticism." The Journal of Religion 24 (1944): 188-200.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Dan, 1985; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ O. N. Rose, "Madonna’s challenge: understanding Kabbalah today." Tikkun 19 (2004); Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Wieder, "The book of Splendor." First Things: A Monthly Journal of Religion and Public Life 167 (2006): 44.
- ↑ B. Balint, "Divine arts." Commentary 12(1)(2006)
- ↑ Balint, 2006; Wieder, 2006.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Balint, 2006.
- ↑ Allison Coudert, “A Cambridge Platonist’s Kabbalist Nightmare,” Journal of the History of Ideas 35 (1975): 633-652.
- ↑ Balint, 2006.
- ↑ Minkin, 1944; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Balint, 2006; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ O.N. Rose, "Madonna’s challenge: understanding Kabbalah today." Tikkun 19 (2004).
- ↑ A. Aczel. The mystery of the Aleph: mathematics, the Kabbalah, and the search for infinity. (New York: Four Walls Eight Windows, 2000. ISBN 978-0743422994); Dan, 1985; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Aczel, 2000.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Arthur Green. Ehyeh: A Kabbalah for Tomorrow. (Jewish Lights Publishing, 2004. ISBN 1580232132)
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Dan, 1985; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ David Cooper. God Is a Verb. (Penguin USA/Riverhead Trade, 1998), 53.
- ↑ Idries Shah. The Sufis. (Octagon Press Ltd, 1999. ISBN 978-0863040740)
- ↑ References to a word related to "qlipoth" are found in some Babylonian incantations, a fact used as evidence to argue the antiquity of kabbalistic material.
- ↑ Balint, 2006; Minkin, 1944; Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Minkin, 1944.
- ↑ Zetter, 1999.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Judaica. Volume 6, "Dualism," 244.
- ↑ In an article that appears in The Seductiveness of Jewish Myth, David Halperin theorizes that the collapse of Kabbalah's influence among Western European Jews over the course of the seventeenth and eighteenth century was a result of the cognitive dissonance they experienced between Kabbalah's very negative perception of Gentiles and their own dealings with non-Jews, which were rapidly expanding and improving during this period due to the influence of the Enlightenment.
- ↑ Rabbi Bradley Shavit Artson,[2], "From the Periphery to the Center: Kabbalah & Conservative Judaism." Ziegler School of Rabbinical Studies in the University of Judaism. Retrieved March 29, 2009.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- This article incorporates text from the 1901–1906 Jewish Encyclopedia, a publication now in the public domain.
- Aczel, A. The mystery of the Aleph: mathematics, the Kabbalah, and the search for infinity. New York: Four Walls Eight Windows, 2000. ISBN 978-0743422994
- Alexenberg, M. "Ancient schema and technoetic creativity." Technoetic Arts: a Journal of Speculative Research 4 (2006): 3–15.
- Balint, B. "Divine arts." Commentary 12(1) (2006).
- Breslauer, S. Daniel (ed.). The Seductiveness of Jewish Myth: Challenge or Response? (Suny Series in Judaica - Hermeneutics, Mysticism and Religion) (1954) reprint State University of New York Press, 1997. ISBN 0791436020
- Cooper, David. God Is a Verb. Riverhead Trade, 1998. ISBN 978-1573226943
- Coudert, Allison. “A Cambridge Platonist’s Kabbalist Nightmare,” Journal of the History of Ideas 35 (1975): 633-652.
- Dan, J. "Gershom Scholem’s reconstruction of early Kabbalah." Modern Judaism 5 (1985): 39–66.
- Fine, L. (ed.). Essential Papers in Kabbalah. New York: NYU Press, 1995. ISBN 978-0814726297
- Fine, L. (ed.). Physician of the Soul, Healer of the Cosmos: Isaac Luria and his Kabbalistic Fellowship. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0804738255
- Fine, L. (ed.). Safed Spirituality, Mahwah, NJ: Paulist Press, 1989. ISBN 978-0809126125
- Fine, L. (ed.). Judaism in Practice. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2001. ISBN 978-0691057873
- Fortune, Dion. Mystical Qabalah. San Francisco, CA: Weiser Books, 2000. ISBN 978-1578631506
- Goldish, M. "Kabbalah, academia, and authenticity." Tikkun 20 (2005): 63-67.
- Green, Arthur. Ehyeh: A Kabbalah for Tomorrow. Jewish Lights Publishing, 2004. ISBN 1580232132
- Idel, Moshe. The Mystical Experience in Abraham Abulafia, New York: SUNY Press, 1988. ISBN 978-0887065538
- Idel, Moshe. Kabbalah: New Perspectives. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1988. ISBN 978-0300046991
- Idel, Moshe. The Golem: Jewish Magical and Mystical Traditions on the Artificial Anthropoid. New York: SUNY Press, 1990. ISBN 978-0791401606
- Idel, Moshe. Hasidism: Between Ecstasy and Magic. New York: SUNY Press, 1995. ISBN 978-0791417348
- Kaplan, Aryeh. Inner Space: Introduction to Kabbalah, Meditation and Prophecy. Moznaim Publishing Corp, 1990. ISBN 978-0940118560
- Minkin, J. "Jewish mysticism." The Journal of Religion 24 (1944): 188-200.
- Rose, O.N. "Madonna’s challenge: understanding Kabbalah today." Tikkun 19 (2004).
- Scholem, Gershom. Kabbalah. Jewish Publication Society. ISBN 978-0880292054
- Shah, Idries. The Sufis. Octagon Press Ltd, 1999. ISBN 978-0863040740
- Tishby, Isaiah (ed.). The Wisdom of The Zohar: An Anthology of Texts. 3 volume set, translated from the Hebrew by David Goldstein, The Littman Library. ISBN 978-1874774280
- Wieder, L. "The book of Splendor." First Things: A Monthly Journal of Religion and Public Life 167(2006): 44.
- Wineberg, Yosef. Lessons in Tanya: The Tanya of R. Shneur Zalman of Liadi. (5 volume set). Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch, 1998. ISBN 978-0826605412
- Zetter, K. Simple Kabbalah. Berkeley: Conari Press, 1999. ISBN 978-0785815112
External links
All links retrieved February 28, 2025.
- Kabbalah and Jewish Mysticism mechon-mamre,org.
- What is Kabbalah? Chabad.org.
- Cabala jewishencyclopedia.com.
- Essay about which Rabbinic Kabbalah texts are available in English
- English and Aramaic Zohar Online (searchable) Zohar.com.
- Lessons in Tanya chabad.org.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.