Northwest Ordinance
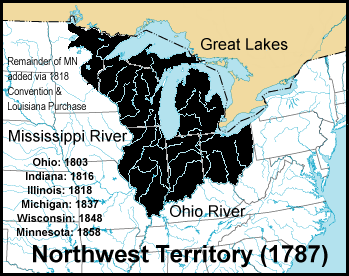
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio, and also known as the Freedom Ordinance) was an act of the Continental Congress of the United States unanimously passed on July 13, 1787 under the Articles of Confederation. The primary effect of the ordinance was the creation of the Northwest Territory as the first organized territory of the United States out of the region south of the Great Lakes north and west of the Ohio River, and east of the Mississippi River. On August 7, 1789, the U.S. Congress affirmed the Ordinance with slight modifications under the Constitution. Arguably the single most important piece of legislation passed by the Continental Congress other than the Declaration of Independence, it established the precedent by which the United States would expand westward across North America by the admission of new states, rather than by the expansion of existing states. The banning of slavery in the territory had the effect of establishing the Ohio River as the boundary between free and slave territory in the region between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River. This division helped set the stage for the balancing act between free and slave states that was the basis of a critical political question in American politics in the nineteenth century until the Civil War.
History
Acquired by Great Britain from France following the 1763 Treaty of Paris, the Ohio Country had been closed to white settlement by the Proclamation of 1763. The United States claimed the region after the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War, but was subject to overlapping and conflicting claims of the states of the Massachusetts, Connecticut, New York, and Virginia, as well as a lingering British presence that was not settled until the War of 1812.
The region had long been desired for expansion by colonists, however, and urgency of the settlement of the claims of the states was prompted in large measure by the de facto opening of the area to settlement following the loss of British control.
In 1784 Thomas Jefferson proposed that the states should relinquish their particular claims to all the territory west of the Appalachians, and the area should be divided into new states of the Union. Jefferson proposed creating seventeen roughly rectangular states from the territory, and even suggested names for the new states, including Chersonesus, Sylvania, Assenisipia, Metropotamia, Polypotamia, Pelisipia, Saratoga, Washington, Michigania and Illinoia. Although the proposal was not adopted, it established the example that would become the basis for the Northwest Ordinance three years later.
Effects of the legislation

Abolition of state claims
The passage of the ordinance forced the relinquishing of all such claims by the states over the territory, which was to be administered directly by Congress, with the intent of eventual admission of newly created states from the territory. The legislation was revolutionary in that it established the precedent for lands to be administered by the central government, albeit temporarily, rather than underneath the jurisdiction of particular states.
Admission of new states
The most significant intended purpose of the legislation was its mandate for the creation of new states from the region, once a population of 60,000 had been achieved within a particular territory. The actual legal mechanism of the admission of new states was established in the Enabling Act of 1802. The first state created from the territory was Ohio, in 1803.
Establishment of territorial government
As an organic act, the ordinance created a civil government in the territory under the direct jurisdiction of the Congress. The ordinance was thus the prototype for the subsequent organic acts that created organized territories during the westward expansion of the United States.
It specifically provided for the appointment by Congress of a territorial governor with a three-year term, a territorial secretary with a four-year term, and three judges, with no set limit to their term. As soon as there was a population of 5,000, they could form a general assembly for a legislature.
In 1789 Congress made minor changes, such that the president, with the advice and consent of the U.S. Senate, had the power to appoint and remove the governor and officers of the territory instead of Congress. Also, the territorial secretary was authorized to act for the governor, if he died, was absent, was removed, or resigned from office.
Establishment of civil rights
The civil rights provisions of the ordinance foreshadowed the Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution. Many of the concepts and guarantees of the Ordinance of 1787 were incorporated in the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights. In the Northwest Territory, various legal and property rights were enshrined, religious tolerance was proclaimed, and "Religion, morality, and knowledge" were enunciated as being "necessary to good government and the happiness of mankind, schools and the means of education." The right of habeas corpus was written into the charter, as was freedom of religious worship and bans on excessive fines and cruel and unusual punishment. Trial by jury and a ban on ex post facto laws were also rights granted.
Prohibition of slavery
The ordinance prohibited slavery in the region, at a time when northeastern states such as New York and New Jersey still permitted it. The text of the ordinance read, "There shall be neither slavery nor involuntary servitude in the said territory, otherwise than in the punishment of crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted." In reality, slaves were (illegally) kept in parts of the territory, and the practice of indentured servitude was tacitly permitted.
In the decades preceding the American Civil War, the abolition of slavery in the northeast by the 1830s created a contiguous region of free states to balance the Congressional power of the slave states in the south. After the Louisiana Purchase, the Missouri Compromise effectively extended the Ohio River boundary between free and slave territory westward from the Mississippi to the Rocky Mountains. The balance between free and slave territory established in the ordinance eventually collapsed following the Mexican-American War.
Many "fire-eater" southerners of the 1850s denied that Congress even had the authority to bar the spread of slavery to the Northwest Territory. President George Washington did not advocate the abolition of slavery while in office, but signed legislation enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the Northwest Territory, writing to his good friend the Marquis de la Fayette that he considered it a wise measure. Thomas Jefferson and James Madison both wrote that they believed Congress had such authority.
Definition of the Midwest as a region
The Northwest Ordinance, along with the Land Ordinance of 1785, laid the legal and cultural groundwork for Midwestern (and subsequently, western) development. Significantly, the Free State legal philosophies of both Abraham Lincoln and Salmon P. Chase (chief justice, senator, and early Ohio law author) were derived from the Northwest Ordinance.
Effects on Native Americans
The Northwest Ordinance also made mention of Native Americans: "The utmost good faith shall always be observed towards the Indians; their land and property shall never be taken without their consent; and, in their property, rights, and liberty, they shall never be invaded or disturbed." However, many American Indians in Ohio refused to recognize the validity of treaties signed after the Revolutionary War that ceded lands north of the Ohio River to the United States. In a conflict sometimes known as the Northwest Indian War, Blue Jacket of the Shawnees and Little Turtle of the Miamis formed a confederation to stop white settlement. After the Indian confederation had killed more than eight hundred soldiers in two devastating battlesâthe worst defeats ever suffered by the U.S. at the hands of Native AmericansâPresident Washington assigned General Anthony Wayne command of a new army, which eventually defeated the confederation and thus allowed whites to continue settling the territory.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Anastaplo, George. Abraham Lincoln: A Constitutional Biography. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 1999. ISBN 9780847694310
- Bowen, Catherine Drinker. Miracle at Philadelphia: The Story of the Constitutional Convention, May to September 1787. Boston, MA: Little, Brown, 1966. ISBN 9780316103985
- Onuf, Peter S. Statehood and union: A History of the Northwest Ordinance. Midwestern History and Culture. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 1987. ISBN 9780253354822
- Taylor, Robert M. The Northwest Ordinance, 1787: A Bicentennial Handbook. Indianapolis, IN: Indiana Historical Society, 1987. ISBN 9780871950086
- Williams, Frederick D. The Northwest Ordinance: essays on its formulation, provisions, and legacy. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University Press, 1989. ISBN 9780870132629
External links
All links retrieved November 16, 2022.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.