Adirondack Mountains
| Adirondack Mountains | |
| Range | |
Lake Placid, in the Adirondack region.
| |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | New York |
| Highest point | Mount Marcy |
| - elevation | 5,344 feet (1,629 meters) |
| - coordinates | |
| Orogeny | Grenville Orogeny |
| Period | Tonian |
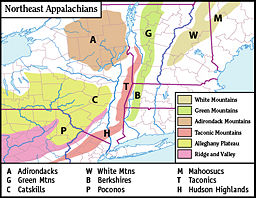
The Adirondack Mountains are a mountain range located in the northeastern part of New York State, extending southward from the Saint Lawrence River valley and Lake Champlain to the Mohawk River valley. They are bordered on the east by Lake Champlain and Lake George, which separate them from the Green Mountains in Vermont. The mountains are often included by geographers in the Appalachian Mountain system, but they are related geologically to Canada's Laurentian Mountains and the Canadian Shield. They were formed approximately one billion years ago and have been subjected to hundreds of millions of years of erosion and glaciation.
The Adirondacks region, which runs through ten counties covering more than 9,400 square miles, is circular in outline and dome-like in appearance. It is comprised of hundreds of peaks and foothills, with more than 40 summits higher than 4,000 feet (1,200 meters).
After more than ten years of recommendations and support for the creation of a forest preserve to protect the region's natural environment, the Adirondack Forest Preserve was created in 1885. This was followed, in 1892, by the establishment of the 6.1 million acre Adirondack Park. In 1894, an amendment to the New York State Constitution was adopted for further protection of the Adirondacks, which reads in part:
The lands of the State … shall be forever kept as wild forest lands. They shall not be leased, sold, or exchanged, nor shall the timber thereon be sold, removed or destroyed.
Further, the language of the article, and decades of legal experience in its defense, are widely recognized as having laid the foundation for the U.S. National Wilderness Act of 1964. As a result of the legal protections, many pieces of the original forest of the Adirondacks have never been logged and are old growth. Only sparsely settled, much of the area remains in a pristine natural state.
Etymology
The name "Adirondacks" is an Anglicized version of the Mohawk ratirontaks, meaning "they eat trees," a derogatory name which the Mohawk historically applied to neighboring Algonquian-speaking tribes; when food was scarce, the Algonquians would eat the buds and bark of trees.[1]
The mountains were given the name "Adirondacks" in 1838 by Ebenezer Emmons;[2] the name is sometimes spelled Adirondaks, without a c. Some of the place names in the vicinity of Lake Placid have peculiar phonetic spellings attributed to Melville Dewey, who was a principal influence in developing that town and the Lake Placid Club. The word carries stress on the third syllable: [ədɪˈɾɔndəks]. A common nickname for the area is "Dacks" or "Dax."
Mountains
The Adirondacks do not form a connected range, but is an eroded dome consisting of many summits, isolated or in groups, often with little apparent order. There are over one hundred summits, ranging from under 1,200 to over 5,000 feet (370 m to 1500 m) in altitude; the highest peak, Mount Marcy (sometimes also called Tahawus), at 5,344 ft (1,629 m), is near the eastern part of the group.
Other noted High Peaks include:
- Algonquin Peak (formerly Mt. McIntyre); 5,114 ft (1,559 m)
- Haystack; 4,960 ft (1,512 m)
- Skylight; 4,926 ft (1,501 m)
- Whiteface; 4,867 ft (1,483 m)
- Dix; 4,857 ft (1,480 m)
- Giant; 4,627 ft (1,410 m)
High peaks
Forty-six of the tallest mountains are considered "The 46" Adirondack High Peaks—those over 4,000 ft (1,219 m), as surveyed at the beginning of the twentieth century. Since that time, better surveys have shown that four of these peaks (Blake Peak, Cliff Mountain, Nye Mountain, and Couchsachraga Peak) are in fact just under 4,000 ft (1,200 m), and one peak just over 4,000 ft (MacNaughton Mountain) was overlooked.
There are many fans of the Adirondack Mountains who make an effort to climb all of the original 46 mountains (and most go on to climb MacNaughton as well), and there is a Forty Sixers club for those who have successfully reached each of these peaks. Twenty of the 46 peaks have no official trail to the top, although rough informal routes, commonly referred to as "herd paths," have developed over the years and no true bushwhacking is required on any of the peaks, although some are still quite primitive.
Atop the highest peaks, above the tree line, there is a total of 87 acres (352,000 m²) of extraordinarily fragile alpine ecosystem; the amount of this ecosystem is constantly changing due to variation in the climate from year to year.
The region contains many alpine lakes and meadows, wetlands, streams, andforests. Unfortunately, the high number of visitors is degrading the natural beauty of some of the more heavily traveled areas of the region, and it has been necessary in recent years to more strictly regulate access and use. The Eastern High Peaks Wilderness area is the most regulated area.
Geography
The Adirondack Mountains are contained within the 6.1 million acres (25,000 km²) of the Adirondack Park, which includes a constitutionally-protected Forest Preserve of approximately 2.3 million acres (9,300 km²). About 43 percent of the land is owned by the state, with 57 percent private inholdings, heavily regulated by the Adirondack Park Agency.[3]
The park contains thousands of streams, brooks and lakes, most famously Lake Placid, adjacent to the village of Lake Placid, two-time site of the Olympic Winter Games, the Saranac Lakes, favored by the sportsmen who made the Adirondacks famous, and Raquette Lake, site of many of the first Great Camps. The surface of many of the lakes lies at an elevation above 1,500 ft (450 m); their shores are usually rocky and irregular, and the wild scenery within their vicinity has made them very popular with tourists.
Lake Placid outflow is a major contributor to the Ausable River, which for a part of its course flows through a rocky chasm 100 feet to 175 feet (30 m to 53 m) deep and rarely more than 30 ft (10 m) wide. At the head of the Ausable Chasm are the Rainbow Falls, where the stream makes a vertical leap of 70 ft (20 m).
An impressive feature of the Adirondacks is Indian Pass, a gorge between Algonquin and Wallface Mountains. The latter is a majestic cliff rising several hundred feet from the pass. Keene Valley, in the center of the High Peaks, is another picturesque region, presenting a combination of peaceful valley and rugged hills.
The heavily forested region is the most southerly distribution of the boreal forest or taiga in the North American continent. The forests of the Adirondacks include spruce, pine, and broad-leafed trees. Lumbering, once an important industry, has been much restricted since the establishment of the State Park in 1892.
Approximately 260 species of birds have been recorded in the park, of which over 170 breed here. Because of its unique boreal forest habitat, the park has many breeding birds not found in most areas of New York and other mid-Atlantic states, such as boreal chickadees, gray jays, Bicknell's thrushes, spruce grouse, Philadelphia vireos, rusty blackbirds, American Three-toed Woodpeckers, black-backed woodpeckers, ruby-crowned kinglets, bay-breasted warblers, mourning warblers, common loons, and the crossbills.
Although the climate during the winter months can be severe, with absolute temperatures sometimes falling below −30 °F (−35 °C) pre wind chill, a number of sanatoriums were located there in the early 1900s because of the positive effect the air had on tuberculosis patients.
Geology

The Adirondack Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian physiographic division.[4]
The mountains consist primarily of metamorphic rocks, mainly gneiss, surrounding a central core of intrusive igneous rocks, most notably anorthosite, in the high peaks region. These crystalline rocks are a lobe of the Precambrian Grenville Basement rock complex and represent the southernmost extent of the Canadian Shield,[5] a cratonic expression of igneous and metamorphic rock 880 million to 1 billion years in age that covers most of eastern and northern Canada and all of Greenland. Although the rocks are ancient, the uplift that formed the Adirondack dome has occurred within the last 5 million years—relatively recent in geologic time—and is ongoing. The dome itself is roughly circular, approximately 160 miles (260 km) in diameter and about one mile (1.6 km) high. The uplift is almost completely surrounded by Palaeozoic strata which lap up on the sides of the underlying basement rocks.[6]
The rate of uplift in the Adirondack dome is the subject of some debate, but in order to have the rocks which constitute the Adirondacks rise from the depth where they were formed to their present height, within the last 20 million years, an uplift rate of 1-3 mm a year is required. This rate is greater than the rate of erosion in the region today and is considered a fairly high rate of movement. Earthquakes in the region have exceeded 5 on the Richter scale.
The mountains form the drainage divide between the Hudson watershed and the Great Lakes Basin/St. Lawrence River watershed. On the south and southwest the waters flow either directly into the Hudson, which rises in the center of the group, or else reach it through the Mohawk River. On the north and east the waters reach the St. Lawrence River by way of Lakes George and Champlain, and on the west they flow directly into that stream or reach it through Lake Ontario. The tiny Lake Tear-of-the-Clouds, nestled in the heart of the High Peaks area between Mt. Marcy and Skylight, is considered to be the source of the mighty Hudson. The most important streams within the area are the Hudson, Black, Oswegatchie, Grasse, Raquette, Saranac, Schroon, and Ausable River rivers.
The region was once covered, with the exception of the higher summits, by the Laurentian Glacier, whose erosion, while perhaps having little effect on the larger features of the country, has greatly modified it in detail, producing lakes and ponds, whose number is said to exceed 1,300, and causing many falls and rapids in the streams. Among the larger lakes are Lake George, The Fulton Chain, the Upper and Lower Saranac, Big and Little Tupper, Schroon, Placid, Long, Raquette, and Blue Mountain. The region known as the Adirondack Wilderness, or the Great North Woods, embraces between 5,000 and 6,000 square miles (13,000 km² and 16,000 km²) of mountain, lake, plateau, and forest.
Mining was once a significant industry in the Adirondacks. The region is rich in magnetic iron ores, which were mined for many years. Other mineral products are graphite, garnet used as an abrasive, pyrite, wollastonite, and zinc ore. There is also a great quantity of titanium, which was mined extensively.
History
Algonquin and Mohawk Indians used the Adirondacks for hunting and travel, but they had no settlements in the area. Samuel de Champlain sailed up the Saint Lawrence River and Rivière des Iroquois near what would become Ticonderoga on Lake Champlain in 1609, and thus may have been the first European to encounter the Adirondacks. Jesuit missionaries and French trappers were among the first Europeans to visit the region, as early as 1642.
Part of the French and Indian War (1754-1763) was played out on the edge of the Adirondacks. The British built Fort William Henry on the south end of Lake George in 1755; the French countered by building Fort Carillon on the north end, which was renamed Fort Ticonderoga after it was captured by the British. In 1757, French General Montcalm, captured Fort William Henry.
At the end of the eighteenth century rich iron deposits were discovered in the Champlain Valley, precipitating land clearing, settlement and mining in that area, and the building of furnaces and forges. A growing demand for timber pushed loggers deeper into the wilderness. Millions of pine, spruce, and hemlock logs were cut and floated down the area's many rivers to mills built on the edges. Logging continued slowly but steadily into the interior of the mountains throughout the 19th century and farm communities developed in many of the river valleys.
The area wasn't formally named the Adirondacks until 1837; an English map from 1761 labels it simply "Deer Hunting Country." Serious exploration of the interior did not occur until after 1870; the headwaters of the Hudson River at Lake Tear of the Clouds near Mount Marcy were not discovered until more than fifty years after the discovery of the headwaters of the Columbia River in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia.
Prior to the nineteenth century, mountainous areas and wilderness were viewed as desolate and forbidding. As Romanticism developed in the United States, the writing of James Fenimore Cooper and later the transcendentalism of Henry David Thoreau and Ralph Waldo Emerson began to transform the popular view of wilderness in more positive terms, as a source of spiritual renewal.
Part of Cooper's 1826, The Last of the Mohicans: A narrative of 1757, is set in the Adirondacks. Frederic Remington canoed the Oswegatchie River, and William James Stillman, painter and journalist, spent the summer of 1857 painting near Raquette Lake. The next year he returned with a group of friends to a spot on Follensby Pond that became known as the Philosophers Camp. The group included Emerson, James Russell Lowell, Louis Agassiz, and Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr.'s brother John.
Although sportsmen had always shown some interest in the Adirondacks, the publication of clergyman William H. H. Murray's Adventures in the Wilderness; Or Camp-Life in the Adirondacks in 1869 started a flood of tourists to the area, leading to a rash of hotel building and the development of stage coach lines. Thomas Clark Durant, who had helped to build the Union Pacific railroad, acquired a large tract of central Adirondack land and built a railroad from Saratoga Springs to North Creek. By 1875 there were more than two hundred hotels in the Adirondacks, some of them with several hundred rooms; the most famous was Paul Smith's Hotel. About this time, the "Great Camps" of the Adirondacks evolved near Raquette Lake, where William West Durant, son of Thomas C. Durant, built luxurious compounds. Two of them, Camp Pine Knot and Sagamore Camp, both near Raquette Lake, have been designated as National Historic Landmarks, as has Santanoni Preserve, near Newcomb, NY. Camps Sagamore and Santanoni are open to the public seasonally.
In 1873, Verplanck Colvin developed a report urging the creation of a state forest preserve covering the entire Adirondack region, based on the need to preserve the watershed as a water source for the Erie Canal, which was vital to New York's economy at the time. In 1883, he was appointed superintendent of the New York State Land Survey. In 1884, a commission chaired by botanist Charles Sprague Sargent recommended establishment of a forest preserve, to be "forever kept as wild forest lands."[7] In 1885, the Adirondack Forest Preserve was created, followed in 1892 by the Adirondack Park. When it became clear that the forces seeking to log and develop the Adirondacks would soon reverse the two measures through lobbying, environmentalists sought to amend the State Constitution. In 1894, Article VII, Section 7, (renumbered in 1938 as Article XIV, Section 1) of the New York State Constitution was adopted, which reads in part:
The lands of the state, now owned or hereafter acquired, constituting the forest preserve as now fixed by law, shall be forever kept as wild forest lands. They shall not be leased, sold or exchanged, or be taken by any corporation, public or private, nor shall the timber thereon be sold, removed or destroyed.[8]
The restrictions on development and lumbering embodied in Article XIV have withstood many challenges from timber interests, hydropower projects, and large scale tourism development interests.[9] Further, the language of the article, and decades of legal experience in its defense, are widely recognized as having laid the foundation for the U.S. National Wilderness Act of 1964. As a result of the legal protections, many pieces of the original forest of the Adirondacks have never been logged: They are old growth.[10]
Tourism and recreation
Cabins, hunting lodges, villas and hotels in the Adirondacks are numerous. The resorts most frequented are in and around Lake Placid, Lake George, Saranac Lake, Schroon Lake, and the St. Regis Lakes.
Hunting and fishing are allowed in the Adirondack Park, although in many places there are strict regulations. Because of these regulations, the large tourist population has not overfished the area, and as such, the brooks, rivers, ponds, and lakes remain well stocked with trout and black bass. Flatwater and whitewater canoeing and kayaking are very popular. Hundreds of lakes, ponds, and slow-moving streams link to provide routes ranging from under a mile to week-long treks.
At the head of Lake Placid stands Whiteface Mountain, from whose summit one of the finest views of the Adirondacks can be obtained. Two miles (3 km) southeast of this lake, at North Elba, is the old farm of the abolitionist John Brown, which contains his grave and is frequented by visitors.
July 4, 2006, marked the dedication and opening celebration of Natural History Museum of the Adirondacks, also known as The Wild Center. The 30 million dollar facility is in Tupper Lake. The new museum, designed by the firm that built the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., has extensive exhibits about the natural history of the region. Many of the exhibits are live, including those of otters, birds, fish, and porcupines. The museum has trails to a river and pond on its campus.
Notes
- ↑ Alfred L. Donaldson, A History of the Adirondacks (BiblioBazaar, 2009, ISBN 978-1115784955).
- ↑ D.J. Cherniak, Ebenezer Emmons (1799-1863), Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Retrieved August 16, 2018.
- ↑ More about the Adirondack Park Adirondack Park Agency. Retrieved August 16, 2018.
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey, Physiographic divisions of the conterminous U.S. Retrieved August 16, 2018.
- ↑ Timothy McDonnell, Physical Geography of New York, New York Geographic Alliance. Retrieved August 16, 2018.
- ↑ Yngvar W. Isachsen (ed.), Geology of New York: A Simplified Account (New York State Museum Press, 2000, ISBN 978-1555571627).
- ↑ Philip G. Terrie, Forever Wild: A Cultural History of Wilderness in the Adirondacks (Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 1994, ISBN 978-0815602934), 98.
- ↑ Article XIV of the New York State Constitution, Department of Environmental Conservation.
- ↑ Neil F. Woodworth, "Recreational Use of the Forest Preserve under the Forever Wild Clause," in Barbara McMartin (ed.), Celebrating the Constitutional Protection of the Forest Preserve: 1894-1994 (Silver Bay, NY: Symposium Celebrating the Constitutional Protection of the Forest Preserve, 1994).
- ↑ Barbara McMartin, The Great Forest of the Adirondacks (Utica, NY: North Country Books, 1994, ISBN 0925168297).
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Donaldson, Alfred L. A History of the Adirondacks. BiblioBazaar, 2009. ISBN 978-1115784955.
- Graham, Frank. The Adirondack Park: A Political History. Syracuse NY: Syracuse Univ Press, 1984. ISBN 978-0815601920.
- Isachsen, Yngvar W. (ed.). Geology of New York: A Simplified Account. New York State Museum Press, 2000. ISBN 978-1555571627
- McKibben, Bill. Hope, Human and Wild: True Stories of Living Lightly on the Earth. Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 1995. ISBN 978-0316560641.
- McMartin, Barbara. The Great Forest of the Adirondacks. Utica, NY: North Country Books, 1994. ISBN 0925168297
- Schaefer, Paul. Defending the Wilderness: The Adirondack Writings of Paul Schaefer. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 1989. ISBN 978-0815602378.
- Schneider, Paul. The Adirondacks: A History of America's First Wilderness. New York: H. Holt and Co., 1997. ISBN 978-0805034905.
- Terrie, Philip G. Forever Wild: A Cultural History of Wilderness in the Adirondacks. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 1994. ISBN 978-0815602934.
- Terrie, Philip G. Contested Terrain a New History of Nature and People in the Adirondacks. Blue Mountain Lake, NY: Adirondack Museum, 1999. ISBN 978-0585275482.
This article incorporates text from the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, a publication now in the public domain.
External links
All links retrieved June 15, 2023.
- NYS Adirondack Park Agency
- Adirondack Museum
- The Wild Center - A Center for the Adirondacks
- Adirondack History
- Adirondack Research Consortium
- Lake George Historical Association
- Adirondack Architectural Heritage
- Association for the Protection of the Adirondacks
- Adirondack Council
- Adirondack Mountain Club
- Adirondack 46ers website
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.