Nikola Tesla
| Nikola Tesla Никола Тесла | |
 "I have harnessed the cosmic rays and caused them to operate a motive device."[1]
| |
| Born | July 10, 1856 Smiljan, Military Frontier, Austrian Empire (modern day Croatia) |
|---|---|
| Died | January 7, 1943 New York City, New York, USA |
| Occupation | inventor, physicist, mechanical engineer and electrical engineer |
Nikola Tesla (Serbian Cyrillic: Никола Тесла) (July 10, 1856 – January 7, 1943) was a world-renowned Serbian-American inventor, physicist, mechanical engineer, and electrical engineer. He is best known for his revolutionary work in and numerous contributions to the discipline of electricity and magnetism in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century. Tesla's patents and theoretical work form the basis of modern alternating current electric power (AC) systems, including the polyphase power distribution systems and the AC motor, with which he helped usher in the Second Industrial Revolution.
In the United States, Tesla's fame rivaled that of any other inventor or scientist in history or popular culture. After his demonstration of wireless communication in 1893 and after being the victor in the "War of Currents," he was widely respected as America's greatest electrical engineer. Much of his early work pioneered modern electrical engineering and many of his discoveries were of groundbreaking importance. In 1943, the Supreme Court of the United States credited him as being the inventor of the radio. Never putting much focus on his finances, Tesla died impoverished and forgotten at the age of 86.
His contribution was recognized and the derived SI unit measuring magnetic flux density or magnetic induction (commonly known as the magnetic field, ), the tesla, was named in his honor (at the Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures, Paris, 1960).
Aside from his work on electromagnetism and engineering, Tesla is said to have contributed in varying degrees to the fields of robotics, ballistics, computer science, nuclear physics, and theoretical physics. In his later years, Tesla was regarded as a mad scientist and became noted for making bizarre claims about possible scientific developments.[2][3] Many of his achievements have been used, with some controversy, to support various pseudosciences, UFO theories, and New Age occultism. Contemporary admirers of Tesla have deemed him "the man who invented the twentieth century."[4]
Early years
According to legend, Tesla was born precisely at midnight during an electrical storm, to a Serbian family in the village of Smiljan near Gospić, in the Lika region of the Austrian Empire, located in present-day Croatia.[5] His baptism certificate reports that he was born on June 28 (N.S. July 10), 1856. His father was Rev. Milutin Tesla, a priest in the Serbian Orthodox Church. His mother was Đuka Mandić, herself a daughter of a Serbian Orthodox Church priest. Tesla was one of five children, having one brother (Dane, who was killed in a horse-riding accident when Nikola was five) and three sisters (Milka, Angelina and Marica).[6] His family moved to Gospić in 1862. Tesla went to school in Karlovac, Croatia then studied electrical engineering at the Austrian Polytechnic in Graz, Austria (1875). While there, he studied the uses of alternating current. It is unclear whether he completed a degree at Graz.
Tesla was later persuaded by his father to attend the Charles-Ferdinand branch of the University of Prague, which he attended for the summer term of 1880. However after his father died he left the university, only completing one term.[7]
Tesla engaged in reading many works, memorizing complete books. He had a photographic memory.[8] Tesla related in his autobiography that he experienced detailed moments of inspiration. During his early life, Tesla was stricken with illness time and time again. He suffered a peculiar affliction in which blinding flashes of light would appear before his eyes, often accompanied by hallucinations. Much of the time the visions were linked to a word or idea he might come across; just by hearing the name of an item, he would involuntarily envision it in realistic detail. Modern-day synesthetes report similar symptoms. Tesla would visualize an invention in his brain in precise form before moving to the construction stage; a technique which is sometimes known as picture thinking. Tesla also often had flashbacks to events that had happened previously in his life, this began to happen during childhood.[8]
Hungary and France
In 1881 he moved to Budapest, Hungary, to work for a telegraph company, the American Telephone Company. There, he met Nebojša Petrović, then a young inventor from Austria. Although their encounter was brief, they did work on a project together using twin turbines to create continual power. On the opening of the telephone exchange in Budapest, 1881, Tesla became the chief electrician to the company, and was later engineer for the country's first telephone system. He also developed a device that, according to some, was a telephone repeater or amplifier, but according to others could have been the first loudspeaker.[9] For a while he stayed in Maribor, Slovenia, where he was first employed as an assistant engineer. He suffered a nervous breakdown during this time. In 1882 he moved to Paris to work as an engineer for the Continental Edison Company, designing improvements to electric equipment. In the same year, Tesla conceived of the induction motor and began developing various devices that use rotating magnetic fields (for which he received patents in 1888).
Soon thereafter, Tesla hastened from Paris to his mother's side as she lay dying, arriving hours before her death in 1882. After her death, Tesla fell ill. He spent two to three weeks recuperating in Gospić and the village of Tomingaj near Gračac, Croatia, the birthplace of his mother.
United States
In 1884, when Tesla first arrived in the U.S., he had little besides a letter of recommendation from Charles Batchelor, his manager in his previous job. In his letter of recommendation to Thomas Edison, Charles Batchelor wrote, "I know two great men and you are one of them; the other is this young man." Edison hired Tesla to work for his company, Edison Machine Works. Tesla's work for Edison began with simple electrical engineering and quickly progressed to solving the company's most difficult problems. Tesla was offered the task of a complete redesign of the Edison company's direct current generators.
In 1919 Tesla wrote that Edison offered him the then-staggering sum of $50,000 (almost $1 million today, adjusted for inflation) if he completed the motor and generator improvements. Tesla said he worked nearly a year to redesign them and gave the Edison company several enormously profitable new patents in the process. When Tesla inquired about the $50,000, Edison reportedly replied to him, "Tesla, you don't understand our American humor," and reneged on his promise.[10] Tesla resigned when he was refused a raise to $25 per week. At Tesla's salary of $18 per week the bonus would have amounted to over 53 years pay, and the amount was equal to the initial capital of the company.[11] He eventually found himself digging ditches for a short period of time—ironically, for Edison’s company. Edison had also never wanted to hear about Tesla's AC polyphase designs, believing that DC electricity was the future. Tesla focused intently on his AC polyphase system, even while digging ditches.[8]
Electromechanical devices and principles developed by Nikola Tesla:[12]
|
Middle years
In 1886, Tesla formed his own company, Tesla Electric Light & Manufacturing. The initial financial investors disagreed with Tesla on his plan for an alternating current motor and eventually relieved him of his duties at the company. Tesla worked in New York City as a common laborer from 1886 to 1887 to feed himself and raise capital for his next project. In 1887 he constructed the initial brushless alternating current induction motor, which he demonstrated to the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (now Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)) in 1888. In the same year, he developed the principles of his Tesla coil and began working with George Westinghouse at Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company's Pittsburgh labs. Westinghouse listened to his ideas for polyphase systems which would allow transmission of alternating current electricity over large distances.
In April 1887, Tesla began investigating what would later be called X-rays using his own single node vacuum tubes, similar to his U.S. Patent 514170 (PDF). This device differed from other early X-ray tubes in that they had no target electrode. The modern term for the phenomenon produced by this device is bremsstrahlung (“braking radiation”). We now know that this device operated by emitting electrons from the single electrode through a combination of field emission and thermionic emission. Once liberated, electrons are strongly repelled by the high electric field near the electrode during negative voltage peaks from the oscillating HV output of the Tesla Coil, generating X-rays as they collide with the glass envelope. He also used Geissler tubes. By 1892, Tesla became aware of what Wilhelm Röntgen later identified as effects of X-rays.
Tesla commented on the hazards of working with single node X-ray producing devices, incorrectly attributing the skin damage to ozone rather than the radiation:
Tesla states that the sunburn effects noted by many experimenters are not due directly to the rays, or Roentgen streams, but to the ozone generated by the rays in contact with the skin. He says "Nitrous acid may also be responsible, to a small extent. The ozone, when abundantly produced, attacks the skin and many organic substances most energetically, the action being no doubt heightened by the heat and moisture of the skin." [14]
Tesla later observed an assistant severely "burnt" by X-rays in his lab. He performed several experiments prior to Röntgen's discovery (including photographing the bones of his hand; later, he sent these images to Röntgen) but didn't make his findings widely known; much of his research was lost in the Fifth Avenue lab fire of March 1895.
On July 30, 1891, he became a naturalized citizen of the United States at the age of 35. Tesla established his Fifth Avenue laboratory in New York during this same year. Later, Tesla would establish his Houston Street laboratory at 46 E. Houston Street. He lit vacuum tubes wirelessly at both of the New York locations, providing evidence for the potential of wireless power transmission.
Some of Tesla's closest friends were artists. He befriended Century Magazine editor Robert Underwood Johnson, who adapted several Serbian poems of Jovan Jovanović Zmaj (which Tesla translated). Also during this time, Tesla was influenced by the Vedic philosophy teachings of the Swami Vivekananda.[15]
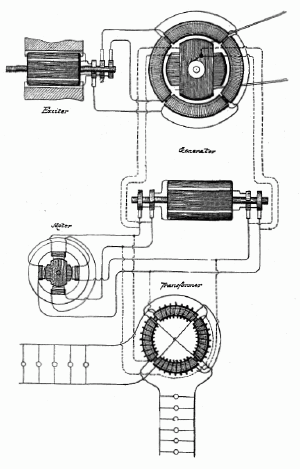
When Tesla was 36 years old, the first patents concerning the polyphase power system were granted. He continued research of the system and rotating magnetic field principles. From 1892 to 1894, Tesla served as vice president of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, the forerunner (along with the Institute of Radio Engineers) to the modern-day Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). From 1893 to 1895, he investigated high frequency alternating currents. He generated AC of one million volts using a conical Tesla coil and investigated the skin effect in conductors, designed tuned circuits, invented a machine for inducing sleep, cordless gas discharge lamps, and transmitted electromagnetic energy without wires, effectively building the first radio transmitter. In Saint Louis, Missouri, Tesla made a demonstration related to radio communication in 1893. Addressing the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and the National Electric Light Association, he described and demonstrated in detail its principles. Tesla's demonstrations were written about widely through various media outlets.
At the 1893 World's Fair in Chicago, an international exposition was held which for the first time devoted a building to electrical exhibits. It was a historic event as Tesla and George Westinghouse introduced visitors to AC power by using it to illuminate the Exposition. On display were Tesla's fluorescent lights and single node bulbs. Tesla also explained the principles of the rotating magnetic field and induction motor by demonstrating how to make an egg made of copper stand on end in his demonstration of the device he constructed known as the "Egg of Columbus."
Also in the late 1880s, Tesla and Edison became adversaries in part due to Edison's promotion of direct current (DC) for electric power distribution over the more efficient alternating current advocated by Tesla and Westinghouse. Until Tesla invented the induction motor, AC's advantages for long distance high voltage transmission were counterbalanced by the inability to operate motors on AC. As a result of the "War of Currents," Edison and Westinghouse went nearly bankrupt, so in 1897, Tesla released Westinghouse from contract, providing Westinghouse a break from Tesla's patent royalties. Also in 1897, Tesla researched radiation which led to setting up the basic formulation of cosmic rays.
When Tesla was 41 years old, he filed the first basic radio patent (U.S. Patent 645576 (PDF)). A year later, he demonstrated a radio controlled boat to the U.S. military, believing that the military would want things such as radio controlled torpedoes. Tesla developed the "Art of Telautomatics," a form of robotics.[10] In 1898 Tesla demonstrated a radio-controlled boat to the public during an electrical exhibition at Madison Square Garden. These devices had an innovative coherer and a series of logic gates. Radio remote control remained a novelty until the 1960s. In the same year, Tesla devised an "electric igniter" or spark plug for Internal combustion gasoline engines. He gained U.S. Patent 609250 (PDF), "Electrical Igniter for Gas Engines," on this mechanical ignition system.
Colorado Springs

In 1899, Tesla decided to move and began research in Colorado Springs, Colorado, where he would have room for his high-voltage, high-frequency experiments. Upon his arrival he told reporters that he was conducting wireless telegraphy experiments transmitting signals from Pikes Peak to Paris. Tesla's diary contains explanations of his experiments concerning the ionosphere and the ground's telluric currents via transverse waves and longitudinal waves.[16] At his lab, Tesla proved that the earth was a conductor, and he produced artificial lightning (with discharges consisting of millions of volts, and up to 135 feet long).[17]
Tesla also investigated atmospheric electricity, observing lightning signals via his receivers. Reproductions of Tesla's receivers and coherer circuits show an unpredicted level of complexity (e.g., distributed high-Q helical resonators, radio frequency feedback, crude heterodyne effects, and regeneration techniques).[18] Tesla stated that he observed stationary waves during this time.[19]
In the Colorado Springs lab, Tesla "recorded" signals of what he believed were extraterrestrial radio signals, though these announcements and his data were rejected by the scientific community. He noted measurements of repetitive signals from his receiver which are substantially different from the signals he had noted from storms and earth noise. Specifically, he later recalled that the signals appeared in groups of one, two, three, and four clicks together. Tesla spent the latter part of his life trying to signal Mars. In 1996 Corum and Corum published an analysis of Jovian plasma torus signals which indicate that there was a correspondence between the setting of Mars at Colorado Springs and the cessation of signals from Jupiter in the summer of 1899 when Tesla was there.[20][21]
Tesla left Colorado Springs on January 7, 1900. The lab was torn down and its contents sold to pay debts. The Colorado experiments prepared Tesla for his next project, the establishment of a wireless power transmission facility that would be known as Wardenclyffe. Tesla was granted U.S. Patent 685012 (PDF) for the means of increasing the intensity of electrical oscillations. The United States Patent Office classification system currently assigns this patent to the primary Class 178/43 ("telegraphy/space induction"), although the other applicable classes include 505/825 ("low temperature superconductivity-related apparatus").
Later years
In 1900, Tesla began planning the Wardenclyffe Tower facility. In June 1902, Tesla's lab operations were moved to Wardenclyffe from Houston Street.
In 1904, the U.S. Patent Office reversed its decision and awarded Guglielmo Marconi the patent for radio, and Tesla began his fight to re-acquire the radio patent. On his 50th birthday in 1906, Tesla demonstrated his 200 horsepower (150 kW) 16,000 rpm bladeless turbine. During 1910–1911 at the Waterside Power Station in New York, several of his bladeless turbine engines were tested at 100–5000 horsepower.
Since the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Marconi for radio in 1909, Thomas Edison and Tesla were mentioned as potential laureates to share the Nobel Prize of 1915 in a press dispatch, leading to one of several Nobel Prize controversies. Some sources have claimed that due to their animosity toward each other neither was given the award despite their enormous scientific contributions and that each sought to minimize the other one's achievements and right to win the award and that both men refused to accept the award if the other received it first, and both rejected any possibility of sharing it.[22] In the following events after the rumors, neither Tesla nor Edison won the prize (although Edison did receive one of 38 possible bids in 1915, and Tesla did receive one bid out of 38 in 1937).[7] Earlier, Tesla alone was rumored to have been nominated for the Nobel Prize of 1912. The rumored nomination was primarily for his experiments with tuned circuits using high-voltage high-frequency resonant transformers.
In 1915, Tesla filed a lawsuit against Marconi attempting, unsuccessfully, to obtain a court injunction against the claims of Marconi. Around 1916, Tesla filed for bankruptcy because he owed so much in back taxes and was living in poverty. After Wardenclyffe, Tesla built the Telefunken Wireless Station in Sayville, Long Island. Some of what he wanted to achieve at Wardenclyffe was accomplished with the Telefunken Wireless. In 1917, the facility was seized and torn down by the United States Marine Corps, because it was suspected that it could be used by German spies.
Prior to World War I, Tesla looked overseas for investors to fund his research. When the war started, Tesla lost the funding he was receiving from his European patents. After the war ended, Tesla made predictions regarding the relevant issues of the post-World War I environment, in a printed article (December 20, 1914). Tesla believed that the League of Nations was not a remedy for the times and issues. Tesla started to exhibit pronounced symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the years following. He became obsessed with the number three; he often felt compelled to walk around a block three times before entering a building and demanded a stack of three folded cloth napkins beside his plate at every meal. The nature of the disorder was little understood at the time and no treatments were available, so his symptoms were considered by some to be evidence of partial insanity, and this undoubtedly hurt what was left of his reputation.
At this time, he was staying at the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel, renting in an arrangement for deferred payments. Eventually, the Wardenclyffe deed was turned over to George Boldt, proprietor of the Waldorf-Astoria, to pay a $20,000 debt. In 1917, around the time that the Wardenclyffe Tower was demolished by Boldt to make the land a more viable real estate asset, Tesla received American Institute of Electrical Engineers's highest honor, the Edison Medal.
In August 1917, Tesla first established principles regarding frequency and power level for the first primitive radar units.[23] In 1934, Émile Girardeau, working with the first French radar systems, stated he was building radar systems "conceived according to the principles stated by Tesla." By the 1920s, Tesla was reportedly negotiating with the United Kingdom government about a ray system. Tesla had also stated that efforts had been made to steal the so called "death ray." It is suggested that the removal of the Chamberlain government ended negotiations.
On Tesla's 75th birthday in 1931, TIME magazine put him on its cover.[24] The cover caption noted his contribution to electrical power generation. Tesla received his last patent in 1928 for an apparatus for aerial transportation which was the first instance of vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft. In 1934, Tesla wrote to consul Janković of his homeland. The letter contained the message of gratitude to Mihajlo Pupin who initiated a donation scheme by which American companies could support Tesla. Tesla refused the assistance, and chose to live by a modest pension received from Yugoslavia and to continue researching.
Field theories
When he was 81, Tesla stated he had completed a dynamic theory of gravity. He stated that it was "worked out in all details" and that he hoped to soon give it to the world.[25] The theory was never published. At the time of his announcement, it was considered by the scientific establishment to exceed the bounds of reason. Most believe that Tesla never fully developed the unified field theory.
The bulk of the theory was developed between 1892 and 1894, during the period that he was conducting experiments with high frequency and high potential electromagnetism and patenting devices for their utilization. It was completed, according to Tesla, by the end of the 1930s. Tesla's theory explained gravity using electrodynamics consisting of transverse waves (to a lesser extent) and longitudinal waves (for the majority). Reminiscent of Mach's principle, Tesla stated in 1925 that:
There is no thing endowed with life - from man, who is enslaving the elements, to the nimblest creature - in all this world that does not sway in its turn. Whenever action is born from force, though it be infinitesimal, the cosmic balance is upset and the universal motion results.
Tesla was critical of Einstein's relativity work, calling it: ...[a] magnificent mathematical garb which fascinates, dazzles and makes people blind to the underlying errors. The theory is like a beggar clothed in purple whom ignorant people take for a king...., its exponents are brilliant men but they are metaphysicists rather than scientists....[26]
Tesla also argued:
I hold that space cannot be curved, for the simple reason that it can have no properties. It might as well be said that God has properties. He has not, but only attributes and these are of our own making. Of properties we can only speak when dealing with matter filling the space. To say that in the presence of large bodies space becomes curved is equivalent to stating that something can act upon nothing. I, for one, refuse to subscribe to such a view.[27]
Tesla also believed that much of Albert Einstein's relativity theory had already been proposed by Ruđer Bošković, stating in an unpublished interview:
...the relativity theory, by the way, is much older than its present proponents. It was advanced over 200 years ago by my illustrious countryman Ruđer Bošković, the great philosopher, who, not withstanding other and multifold obligations, wrote a thousand volumes of excellent literature on a vast variety of subjects. Bošković dealt with relativity, including the so-called time-space continuum...[28]
Directed-energy weapon
Later in life, Tesla made some remarkable claims concerning a "teleforce" weapon[29] The press called it a "peace ray" or death ray.[30][31]
In total, the components and methods included:[32]
- An apparatus for producing manifestations of energy in free air instead of in a high vacuum as in the past. This, according to Tesla in 1934, was accomplished.
- A mechanism for generating tremendous electrical force. This, according to Tesla, was also accomplished.
- A means of intensifying and amplifying the force developed by the second mechanism.
- A new method for producing a tremendous electrical repelling force. This would be the projector, or gun, of the invention.
Tesla worked on plans for a directed-energy weapon between the early 1900s until the time of his death. In 1937, Tesla composed a treatise entitled The Art of Projecting Concentrated Non-dispersive Energy through the Natural Media concerning charged particle beams.[7] Tesla published the document in an attempt to expound on the technical description of a "superweapon that would put an end to all war." This treatise of the particle beam is currently in the Nikola Tesla Museum archive in Belgrade. It described an open ended vacuum tube with a gas jet seal that allowed particles to exit, a method of charging particles to millions of volts, and a method of creating and directing nondispersive particle streams (through electrostatic repulsion).[7]
Records of his indicate that it was based on a narrow stream of atomic clusters of liquid mercury or tungsten accelerated via high voltage (by means akin to his magnifying transformer). Tesla gave the following description concerning the particle gun's operation:
[The nozzle would] send concentrated beams of particles through the free air, of such tremendous energy that they will bring down a fleet of 10,000 enemy airplanes at a distance of 200 miles from a defending nation's border and will cause armies to drop dead in their tracks.[33]
The weapon could be used against ground based infantry or for antiaircraft purposes.[34]
Tesla tried to interest the U.S. Department of War in the device.[35] He also offered this invention to European countries.[36] None of the governments purchased a contract to build the device, and he was unable to act on his plans.
Theoretical inventions
Tesla began to theorize about electricity and magnetism's power to warp or change space and time and the procedure by which man could forcibly control this power. Near the end of his life, Tesla was fascinated with the idea of light as both a particle and a wave, a fundamental proposition already incorporated into quantum physics. This field of inquiry led to the idea of creating a "wall of light" by manipulating electromagnetic waves in a certain pattern. This mysterious wall of light would enable time, space, gravity and matter to be altered at will, and engendered an array of Tesla proposals that seem to leap straight out of science fiction, including anti-gravity airships, teleportation, and time travel. The single strangest invention Tesla ever proposed was probably the "thought photography" machine. He reasoned that a thought formed in the mind created a corresponding image in the retina, and the electrical data of this neural transmission could be read and recorded in a machine. The stored information could then be processed through an artificial optic nerve and played back as visual patterns on a viewscreen.
Another of Tesla's theorized inventions is commonly referred to as “Tesla's Flying Machine." Tesla claimed that one of his life goals was to create a flying machine that would run without the use of an airplane engine, wings, ailerons, propellers, or an on-board fuel source. Initially, Tesla pondered about the idea of a flying craft that would fly using an electric motor powered by grounded base stations. As time progressed, Tesla suggested that perhaps such an aircraft could be run entirely mechanically. The theorized appearance would typically take the form of a cigar or saucer. This fact later enticed UFO conspiracy theorists.
Death and afterwards
Tesla died of heart failure alone in the New Yorker Hotel, some time between the evening of January 5 and the morning of January 8, 1943, at the age of 86. Despite selling his AC electricity patents, Tesla was essentially destitute and died with significant debts. Later that year the United States Supreme Court upheld Tesla's patent number, U.S. Patent 645576 (PDF), in effect recognizing him as the inventor of radio.
Immediately after Tesla's death became known, the Federal Bureau of Investigation instructed the government's Alien Property Custodian office to take possession of his papers and property, despite his U.S. citizenship. His safe at the hotel was also opened. At the time of his death, Tesla had been continuing work on the “teleforce” weapon, or “death ray,” that he had unsuccessfully marketed to the US War Department. It appears that his proposed death ray was related to his research into ball lightning and plasma and was composed of a particle beam weapon. The U.S. government did not find a prototype of the device in the safe. After the FBI was contacted by the War Department, his papers were declared to be top secret. The so-called "peace ray" constitutes a part of some conspiracy theories as a means of destruction. The personal effects were seized on the advice of presidential advisors, and J. Edgar Hoover declared the case "most secret," because of the nature of Tesla's inventions and patents. One document states that "[he] is reported to have some 80 trunks in different places containing transcripts and plans having to do with his experiments [...]." Charlotte Muzar reported that there were several "missing" papers and property.[37]
Tesla's family and the Yugoslav embassy struggled with the American authorities to gain these items after his death due to the potential significance of some of his research. Eventually, his nephew, Sava Kosanoviċ, got possession of some of his personal effects which are now housed in the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade, Serbia.[38] Tesla's funeral took place on January 12, 1943, at the Cathedral of Saint John the Divine in Manhattan, New York City. After the funeral, his body was cremated. His ashes were taken to Belgrade in 1957. The urn was placed in the Nikola Tesla Museum, where it resides to this day.
Tesla did not like to pose for portraits. He did it only once for princess Vilma Lwoff-Parlaghy, but that portrait is lost. His wish was to have a sculpture made by his close friend, Croat Ivan Meštrović, who was at that time in United States, but he died before getting a chance to see it. Meštrović made a bronze bust (1952) that is held in the Nikola Tesla Museum and a statue (1955-1956) placed at the Ruđer Bošković Institute in Zagreb. This statue was moved to Nikola Tesla Street in Zagreb's city centre on the 150th anniversary of Tesla's birth, with the Ruđer Bošković Institute to receive a duplicate. In 1976, a bronze statue of Tesla was placed at Niagara Falls, New York. A similar statue was also erected in his hometown of Gospić in 1986.
The year of 2006 was celebrated by UNESCO as the 150th anniversary of the birth of Nikola Tesla, as well as being proclaimed by the governments of Croatia and Serbia to be the “Year of Tesla.” On this anniversary, July 10, 2006, the renovated village of Smiljan (which had been demolished during the wars of the 1990s) was opened to the public along with Tesla's house (as a memorial museum) and a new multimedia center dedicated to the life and work of Tesla. The parochial church of St. Peter and Paul, where Tesla's father had held services, was renovated as well. The museum and multimedia center are filled with replicas of Tesla's work. The museum has collected almost all of the papers ever published by and about Tesla; most of these provided by Ljubo Vujovic from the Tesla Memorial Society in New York.[39] Alongside Tesla's house, a monument created by sculptor Mile Blazevic has been erected. In the nearby city of Gospić, on the same date as the reopening of the renovated village and museums, a higher education school named for Tesla was opened, and a replica of the statue of Tesla made by Frano Krsinic (the original is in Belgrade) was presented.
In the years after, many of his innovations, theories and claims have been used, at times unsuitably and with some controversy, to support various fringe theories that are regarded as unscientific. Most of Tesla's own work conformed with the principles and methods accepted by science, but his extravagant personality and sometimes unrealistic claims, combined with his unquestionable genius, have made him a popular figure among fringe theorists and believers in conspiracies about “hidden knowledge.” Some conspiracy theorists even in his time believed that he was actually an angelic being from Venus sent to Earth to reveal scientific knowledge to humanity.[8]
Personality
Tesla was fluent in many languages. Along with Serbian/Croatian, he also spoke seven other foreign languages: Czech, English, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, and Latin.
Tesla had a distinct look. He was very tall for his time, towering at six feet seven inches. Tesla was slender, fair-skinned, with pale blue eyes and "wavy brown hair," which he would always wear brushed back briskly. He dressed formally everywhere, often sporting a Prince Albert coat and a derby hat.
Tesla, an obsessive-compulsive, had many unusual quirks and phobias. He did things in threes, and was adamant about staying in a hotel room with a number divisible by three. Tesla was also noted to be physically revolted by jewelry, notably pearl earrings. He was fastidious about cleanliness and hygiene, and was by all accounts germaphobic. He had a great dislike of touching round objects and human hair other than his own.
Tesla was obsessed with pigeons, ordering special seeds for the pigeons he fed in Central Park and even bringing some into his hotel room with him. Tesla was an animal-lover, often reflecting contently about a childhood cat, "The Magnificent Macak" as he would call it.
Except at formal dinners, he always dined alone, and never, under any circumstances, would he dine with a woman by himself. At the Waldorf-Astoria and at the famous Delmonico's restaurant, he had picked out particular discrete tables, which were always reserved for him, along with eighteen clean linen napkins upon his request.
Tesla never married. He was celibate and claimed that his chastity was very helpful to his scientific abilities.[8] Nonetheless, there have been numerous accounts of women vying for Tesla's affection, even some madly in love with him. Tesla, though polite, behaved rather ambivalently to these women in the romantic sense.
Tesla was prone to alienating himself and was generally soft-spoken. However, when he did engage in a social life, many people spoke very positively and admiringly of him. Robert Underwood Johnson described him as attaining a "distinguished sweetness, sincerity, modesty, refinement, generosity, and force..." His loyal secretary, Dorothy Skerrit, wrote "his genial smile and nobility of bearing always denoted the gentlemanly characteristics that were so ingrained in his soul." Tesla's friend Hawthorne wrote that, "seldom did one meet a scientist or engineer who was also a poet, a philosopher, an appreciator of fine music, a linguist, and a connoisseur of food and drink."
Strangely, Tesla displayed occasional streaks of cruelty that seemed to be motivated by his obsessive-compulsiveness. Overweight people disgusted him, and he made little effort to conceal his feelings, once firing a secretary because of her weight. He was quick to criticize clothing as well, demanding a subordinate to go home and change her dress on several occasions.
Tesla was widely known for his great showmanship, presenting his innovations and demonstrations to the public as an artform, almost like a magician. This seems to conflict with his observed reclusiveness; Tesla was a complicated figure. He refused to hold conventions without his Tesla coil blasting electricity throughout the room, despite the audience often being terrified, though he assured them everything was perfectly safe.
In his middle life, Tesla became very close friends with Mark Twain. They spent a lot of time together in his lab and elsewhere. He remained bitter in the aftermath of his incident with Edison. The day after Edison died, The New York Times contained extensive coverage of Edison's life, with the only negative opinion coming from Tesla who was quoted as saying, "He had no hobby, cared for no sort of amusement of any kind and lived in utter disregard of the most elementary rules of hygiene."[8] Tesla continued:
His method was inefficient in the extreme, for an immense ground had to be covered to get anything at all unless blind chance intervened and, at first, I was almost a sorry witness of his doings, knowing that just a little theory and calculation would have saved him 90 per cent of the labor. But he had a veritable contempt for book learning and mathematical knowledge, trusting himself entirely to his inventor's instinct and practical American sense.[40]
As Edison was a very old man, he went as far as to say that looking back, his biggest mistake he had made was never respecting Tesla or his work. This did little for their almost non-existent relationship.
Tesla was also good friends with Robert Underwood Johnson. He had amicable relations with Francis Marion Crawford, Stanford White, Fritz Lowenstein, George Scherff, and Kenneth Swezey.
Tesla made his first million at the age of 40, but gave away nearly all his royalties on future innovations. Tesla was rather inept at finances, but he was almost entirely unconcerned with material wealth to counter this. He ripped up a Westinghouse contract that would have made him the world's first billionaire, in part because of the implications it would have on his future vision of free power, and in part because it would run Westinghouse out of business and Tesla had no desire to deal with the creditors.
Tesla lived the last ten years of his life in a two-room suite on the 33rd floor of the Hotel New Yorker, room 3327. There, near the end of his life, when Tesla was slipping into what many consider an altered state of mind, he would claim to be visited by a specific white pigeon daily. The pigeon, Tesla would say, was very precious to him. As the story goes, one day the white pigeon fell ill. Tesla attempted to nurse it back to health, but it died in his hands. Tesla was not a religious man in the traditional Christian fashion; he believed that there must be a scientific explanation for everything. But when that white pigeon died, Tesla swears he saw a very bright light coming out of its eyes, so bright that even he could not have managed to create so luminous a light. It made him believe that the white pigeon was of something spiritual in origin. Several biographers note that Tesla viewed the death of the pigeon as a "final blow" to himself and his work.
Tesla believed that war could not be avoided until the cause for its recurrence was removed, but was opposed to wars in general.[41] He sought to reduce distance, such as in communication for better understanding, transportation, and transmission of energy, as a means to ensure friendly international relations.[42]
He predicted that:
One day man will connect his apparatus to the very wheel work of the universe... and the very forces that motivate the planets in their orbits and cause them to rotate will rotate his own machinery.[43]
Like many of his era, Tesla, a life-long bachelor, became a proponent of a self-imposed selective breeding version of eugenics. In a 1937 interview, he stated,
...man's new sense of pity began to interfere with the ruthless workings of nature. The only method compatible with our notions of civilization and the race is to prevent the breeding of the unfit by sterilization and the deliberate guidance of the mating instinct...The trend of opinion among eugenists is that we must make marriage more difficult. Certainly no one who is not a desirable parent should be permitted to produce progeny. A century from now it will no more occur to a normal person to mate with a person eugenically unfit than to marry a habitual criminal.[44]
In a 1926 interview, Tesla, commenting on the ills of the social subservience of women and the struggle of women toward gender equality, indicated that humanity's future would be run by "Queen Bees." He believed that women would become the dominant sex in the future.[45]
In his later years Tesla became a vegetarian. In an article for Century Illustrated Magazine, he wrote, "It is certainly preferable to raise vegetables, and I think, therefore, that vegetarianism is a commendable departure from the established barbarous habit." Tesla argued that it is wrong to eat uneconomic meat when large amounts of people are starving; he also believed that plant food was "superior to it [meat] in regard to both mechanical and mental performance." He also argued that animal slaughter was "wanton and cruel."[46]
Recognition and honors
- Scientific societies
As the result of his achievements in the development of electricity and radio, Tesla received many awards and accolades. He was selected as a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), at the time the American Institute of Electrical Engineers) and was awarded its most prestigious prize, the Edison Medal. He was also made a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and accepted invitations to become a member of the American Philosophical Society, and the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts. Because of his research in electrotherapy and his invention of high frequency oscillators, he was also made a fellow of the American Electro-Therapeutic Association.
- SI Unit
The scientific compound derived SI unit measuring magnetic flux density or magnetic induction (commonly known as the magnetic field ), the tesla, was named in his honor (at the Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures, Paris, 1960).
- IEEE Nikola Tesla Award
In 1975 the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) created a Nikola Tesla Award via an agreement between the IEEE Power Engineering Society and the IEEE Board of Directors. It is given to individuals or a team that has made outstanding contributions to the generation or utilization of electric power. The Tesla award is considered the most prestigious award in the area of electric power.[47]
- Doctor Honoris Causa
For his work Tesla received numerous honorary doctoral degrees from a number of universities.
- Yugoslavian/Serbian currency
Tesla was featured on the currency of the former Yugoslavia. The current 100 Serbian dinar banknotes issued by the National Bank of Serbia have a picture Tesla on the obverse (front side). On the reverse side there is portion of drawing of an induction motor from his patent application and a photograph of Tesla holding a [gas filled tube] emitting light as a result of electric induction.
- Cosmological objects
The Tesla crater on the far side of the Moon and the minor planet 2244 Tesla are named in his honor.
- Electric Car
Tesla Motors, an electric car company that is producing high end sports cars, named their company in tribute to Tesla: "The namesake of our Tesla Roadster is the genius Nikola Tesla...We‘re confident that if he were alive today, Nikola Tesla would look over our car and nod his head with both understanding and approval."[48]
Notes
- ↑ Manu Mitra, Nikola Tesla's Free Electricity Electronic Circuit Journal of Electronics and Communication 1(1) (2018). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ David Hatcher Childress (ed.), The Tesla Papers: Nikola Tesla on Free Energy & Wireless Transmission of Power (Kempton, IL: Adventures Unlimited Press, 2000, ISBN 0932813860).
- ↑ Robert Lomas, “The Essay: Spark of Genius,” Independent Magazine (August 21, 1999). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Robert Lomas, The Man who Invented the Twentieth Century (London: Headline Book Publishers, 1999, ISBN 0747275882).
- ↑ Carol Dommermuth-Costa, Nikola Tesla: A Spark of Genius (Minneapolis, MN: Lerner Publications, 1994, ISBN 0822549204), 11-12.
- ↑ Margaret Cheney and Robert Uth, Tesla: Master of Lightning (Monroe Township, NJ: Barnes & Noble, 1999, ISBN 0760710058), 3.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Marc Seifer, Wizard: The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla; Biography of a Genius (Secaucus, NJ: Carol Publishing Group, 1996, ISBN 1559723297).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Margaret Cheney, Tesla: Man Out of Time (New York: Touchstone, 2001, ISBN 0743215362).
- ↑ “Did Tesla really invent the loudspeaker?” Twenty First Century Books. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Nikola Tesla, Ben Johnson (ed.), My Inventions (New York: Barnes & Noble, 1995, ISBN 0760700850).
- ↑ Jill Jonnes, "Empire of Light" (New York: Random House, 2004, ISBN 0375758844), 110.
- ↑ Hugo Gernsback, Nikola Tesla and his inventions Electrical Experimenter, 1919. Scan of article available from The Tesla Society. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Tesla's invention of the AND logic gate Twenty First Century Books. Retrieved July 14, 2021. This pertains to two U.S. patents, U.S. Patent 723188 (PDF) and U.S. Patent 725605 (PDF).
- ↑ Nanette South Clark, Nikola Tesla - X-Ray Experiments, Blindness and Fertilizers Manufactured by Electricity An Engineer's Aspect. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Toby Grotz, The Influence of Vedic Philosophy on Nikola Tesla's Understanding of Free Energy Theoretical Electromagnetic Studies and Learning Association.
- ↑ Nikola Tesla, The True Wireless Electrical Experimenter (May 1919). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Charles Coulston Gillispie, “Tesla, Nikola,” Dictionary of Scientific Biography (New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1975, ISBN 0684101211).
- ↑ Kenneth L. Corum, James F. Corum, and Abdul Hamid Aidinejad, Atmospheric Fields, Tesla's Receivers and Regenerative Detectors (1994).
- ↑ Kenneth L. Corum and James F. Corum, Nikola Tesla, Lightning Observations, and Stationary Waves (1994).
- ↑ Nikola Tesla, Talking with Planets Collier's Weekly (February 19, 1901). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Kenneth L. Corum and James F. Corum, Nikola Tesla and The Planetary Radio Signals The Tesla Society. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ John J. O'Neill, Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla (Lulu Press, 2018, ISBN 0359045146), 228-229.
- ↑ R.M. Page, "The Early History of RADAR," Proceedings of the IRE 50(5) (May 1962).
- ↑ Photo of the cover of TIME magazine The Tesla Society. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Prepared Statement by Nikola Tesla Inventions and Experiments of Nikola Tesla. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Tesla, 79, Promises to Transmit Force New York Times, July 11, 1935. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Marc J. Seifer, Einstein vs Tesla New Dawn Magazine. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Quoted in Leland I. Anderson (ed.), Nikola Tesla: Lecture Before the New York Academy of Sciences April 6, 1897: The Streams of Lenard and Roentgen and Novel Apparatus for Their Production (Breckenridge, CO: Twenty First Century Books, 1994, ISBN 096360127X).
- ↑ Tesla's Ray TIME (July 23, 1934). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Tesla, at 78, Bares New 'Death-Beam' New York Times (July 11, 1934). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Tesla Invents Peace Ray New York Sun (July 10, 1934). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Death-Ray Machine Described New York Sun (July 11, 1934). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Joseph W. Alsop, Jr., Beam to Kill Army at 200 Miles, Tesla's Claim on 78th Birthday New York Herald Tribune (July 11, 1934). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ 'Death Ray' for Planes New York Times (September 22, 1940). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Aerial Defense 'Death-Beam' Offered to U.S. By Tesla Baltimore Sun (July 12, 1940). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ John J. O'Neill, Tesla Tries To Prevent World War II (unpublished chap. 34 of Prodigal Genius). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ http://www.teslasociety.com/muzar.htm Tesla Memorial Society of New York. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Nikola Tesla Museum. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Tesla Memorial Society of New York Retrieved July 14, 200721.
- ↑ Tim Law, The Future of Thermal Comfort in an Energy-Constrained World (Springer, 2015, ISBN 3319033336).
- ↑ H. Winfield Secor, Tesla's Views on Electricity and the War Electrical Experimenter 5(4) (August 1917). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ A Giant Eye to See Around the World Albany Telegram (February 25, 1923). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Liliana Usvat, The Genius Nicola Tesla and Mathematics Mathematics Magazine. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ George Sylvester Viereck and Nikola Tesla, A Machine to End War - A Famous Inventor, Picturing Life 100 Years from Now, Reveals an Astounding Scientific Venture Which He Believes Will Change the Course of History Liberty (February 1937). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ John B. Kennedy, When Woman is Boss, An Interview with Nikola Tesla Collier's Weekly (January 30, 1926). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Nikola Tesla, The Problem of Increasing Human Energy Century Illustrated Magazine (June 1900). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ IEEE Nikola Tesla Award Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ↑ Why the Name "Tesla"? Tesla Motors. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Anderson, Leland I. (ed.). Nikola Tesla: Lecture Before the New York Academy of Sciences April 6, 1897: The Streams of Lenard and Roentgen and Novel Apparatus for Their Production. Breckenridge, CO: Twenty First Century Books, 1994. ISBN 096360127X
- Anderson, Leland I. Priority in Invention of Radio, Tesla v. Marconi. Antique Wireless Association, 1980.
- Cheney, Margaret. Tesla: Man Out of Time. New York: Touchstone, 2001. ISBN 0743215362
- Cheney, Margaret, and Robert Uth. Tesla: Master of Lightning. Monroe Township, NJ: Barnes & Noble, 1999. ISBN 0760710058
- Childress, David Hatcher (ed.). The Tesla Papers: Nikola Tesla on Free Energy & Wireless Transmission of Power. Kempton, IL: Adventures Unlimited Press, 2000. ISBN 0932813860
- Corum, Kenneth L., and James F. Corum. Nikola Tesla, Lightning Observations, and Stationary Waves. 1994. OCLC 68213460
- Corum, Kenneth L., James F. Corum, and Abdul Hamid Aidinejad. Atmospheric Fields, Tesla's Receivers and Regenerative Detectors. 1994. OCLC 68215290
- Dommermuth-Costa, Carol. Nikola Tesla: A Spark of Genius. Minneapolis, MN: Lerner Publications, 1994. ISBN 0822549204
- Gillispie, Charles Coulston. Dictionary of Scientific Biography. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1975. ISBN 0684101211
- Grotz, Toby. “The Influence of Vedic Philosophy on Nikola Tesla's Understanding of Free Energy” Theoretical Electromagnetic Studies and Learning Association. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Jonnes, Jill. Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the World. New York: Random House, 2004. ISBN 0375758844
- Kennedy, John B. “When Woman is Boss, An Interview with Nikola Tesla." Collier's Weekly (January 30, 1926). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Law, Tim. The Future of Thermal Comfort in an Energy-Constrained World. Springer, 2015. ISBN 3319033336
- Lomas, Robert. “The Essay: Spark of Genius.” Independent Magazine (August 21, 1999). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Lomas, Robert. The Man Who Invented the Twentieth Century: Nikola Tesla, forgotten genius of electricity. London: Headline Book Publishers, 1999. ISBN 0747275882
- Martin, Thomas Commerford. The Inventions, Researches, and Writings of Nikola Tesla. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1993. ISBN 088029812X
- Nichelson, Oliver. Tesla's Fuelless Generator and Wireless Power Transmission. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- O'Neill, John J. Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla. Lulu Press, 2018. ISBN 0359045146
- Secor, H. Winfield. "Tesla's Views on Electricity and the War" Electrical Experimenter 5(4) (August 1917). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Seifer, Marc. Wizard: The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla; Biography of a Genius. Secaucus, NJ: Carol Publishing Group, 1996. ISBN 1559723297
- Seifer, Marc J., and Michael Behar. “Electric Mind,” Wired Magazine (October 1998). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Tesla, Nikola. "The Problem of Increasing Human Energy." Century Illustrated Magazine (June 1900). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Tesla, Nikola. “The True Wireless,” Electrical Experimenter (May 1919). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Tesla, Nikola, Ben Johnson (ed.). My Inventions. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1995. ISBN 0760700850
- Viereck, George Sylvester and Nikola Tesla. A Machine to End War Liberty (February 1937). Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Weisstein, Eric W. Tesla, Nikola (1856-1943) Science World. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
External links
All links retrieved November 14, 2022.
- The Tesla Memorial Society
- The Tesla Memorial Society of New York
- The Nikola Tesla Museum
- Works by Nikola Tesla. Project Gutenberg
- The Complete Nikola Tesla U.S. Patent Collection by Jim Bieberich
- Tesla Research – Lost Arts Media
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.




